Page 167 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 167
ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables 3
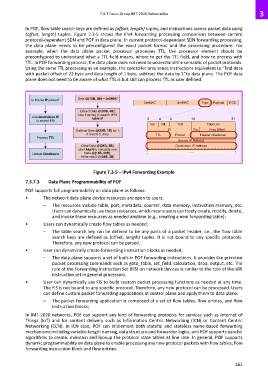
In POF, flow table search keys are defined as {offset, length} tuples, and instructions access packet data using
{offset, length} tuples. Figure 7.3-5 shows the IPv4 forwarding processing comparison between current
protocol-dependent SDN and POF in data plane. In current protocol-dependent SDN forwarding processing,
the data plane needs to be preconfigured the exact packet format and the processing procedure. For
example, when the data plane packet processor processes TTL, the processor element should be
preconfigured to understand what a TTL field means, where to get the TTL field, and how to process with
TTL. In POF forwarding process, the data plane does not need to understand the semantic of packet protocols.
Using the same TTL processing as an example, the controller only sends instructions equivalent to “find data
with packet offset of 22 byte and data length of 1 byte, subtract the data by 1”to data plane. The POF data
plane does not need to be aware of what TTL is but still can process TTL as user defined.
Is this an IP packet? Data @{12B, 2B} = 0x0800?
DstMAC SrcMAC Type Payload FCS
Extract Data @{30B, 4B};
Use it as key to search LPM
Use destination IP table M 0 4 8 16 31
to search FIB
Ver IHL ToS Total Len
Subtract Data @{22B, 1B} by 1; ID Flg Frag Offset
if results 0, drop TTL Protocl Header Checksum
Process TTL
Source IP Address
Clear Data @{24B, 2B}; Destination IP Address
User Alg N to calculate over ……
Update Checksum Data @{14B, 20B};
Write result @{24B, 2B}
Figure 7.3-5 – IPv4 Forwarding Example
7.3.7.3 Data Plane Programmability of POF
POF supports full programmability on data plane as follows:
• The network data plane device resources are open to users;
– The resources include table, port, metadata, counter, data memory, instruction memory, etc.
Users can dynamically use these resources, which means users can freely create, modify, delete,
and invoke these resources as needed anytime (e.g., creating a new forwarding table);
• Users can dynamically create flow tables as needed;
– The table search key can be defined to be any parts of a packet header. i.e., the flow table
search keys are defined as {offset, length} tuples. It is not bound to any specific protocols.
Therefore, any new protocol can be parsed.
• User can dynamically create forwarding instruction blocks as needed;
– The data plane supports a set of built-in POF forwarding instructions. It provides the primitive
packet processing commands such as goto_table, set_field, calculation, drop, output, etc. The
role of the Forwarding Instruction Set (FIS) on network devices is similar to the role of the x86
instruction set in general processors.
• User can dynamically use FIS to build custom packet processing functions as needed at any time.
The FIS is not bound to any specific protocol. Therefore, any new protocol can be processed. Users
can define custom packet forwarding applications at control plane and apply them to data plane;
– The packet forwarding application is composed of a set of flow tables, flow entries, and flow
instruction blocks;
In IMT-2020 networks, POF can support any kind of forwarding protocols for services such as Internet of
Things (IoT) and for content delivery such as Information Centric Networking (ICN) or Content Centric
Networking (CCN). In ICN case, POF can implement both stateful and stateless name-based forwarding
mechanisms including variable-length naming, data structure and forwarder logics, and POF supports parallel
algorithms to create, maintain and lookup the protocol state tables at line rate. In general, POF supports
dynamic programmability on data plane to enable processing any new protocol packets with flow tables, flow
forwarding instruction block and flow entries.
161