Page 166 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 166
3 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
Ring buffer
NIC RX buffer NIC TX buffer
Flow lookup Ring buffer
packet processing
NIC 1 NIC 1
RX CPU2
I/O RX I/O TX TX
CPU0 CPU6
NIC 2 Flow lookup NIC 2
RX packet processing TX
CPU3
NIC 3 NIC 3
RX I/O RX Flow lookup I/O TX TX
CPU1 packet processing CPU7
NIC 4 CPU4 NIC 4
RX
TX
Flow lookup
packet processing
CPU5
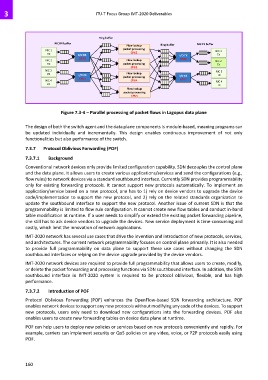
Figure 7.3-4 – Parallel processing of packet flows in Lagopus data plane
The design of both the switch agent and the data plane components is module-based, meaning programs can
be updated individually and incrementally. This design enables continuous improvement of not only
functionalities but also performance of the switch.
7.3.7 Protocol Oblivious Forwarding (POF)
7.3.7.1 Background
Conventional network devices only provide limited configuration capability. SDN decouples the control plane
and the data plane. It allows users to create various applications/services and send the configurations (e.g.,
flow rules) to network devices via a standard southbound interface. Currently SDN provides programmability
only for existing forwarding protocols. It cannot support new protocols automatically. To implement an
application/service based on a new protocol, one has to 1) rely on device vendors to upgrade the device
code/implementation to support the new protocol, and 2) rely on the related standards organization to
update the southbound interface to support the new protocol. Another issue of current SDN is that the
programmability is limited to flow rule configuration. It cannot create new flow tables and conduct in-band
table modification at runtime. If a user needs to simplify or extend the existing packet forwarding pipeline,
she still has to ask device vendors to upgrade the devices. New service deployment is time-consuming and
costly, which limit the innovation of network applications.
IMT-2020 network has several use cases that drive the invention and introduction of new protocols, services,
and architectures. The current network programmability focuses on control plane primarily. It is also needed
to provide full programmability on data plane to support these use cases without changing the SDN
southbound interfaces or relying on the device upgrade provided by the device vendors.
IMT-2020 network devices are required to provide full programmability that allows users to create, modify,
or delete the packet forwarding and processing functions via SDN southbound interface. In addition, the SDN
southbound interface in IMT-2020 system is required to be protocol oblivious, flexible, and has high
performance.
7.3.7.2 Introduction of POF
Protocol Oblivious Forwarding (POF) enhances the OpenFlow-based SDN forwarding architecture. POF
enables network devices to support any new protocols without modifying any code of the devices. To support
new protocols, users only need to download new configurations into the forwarding devices. POF also
enables users to create new forwarding tables on device data plane at runtime.
POF can help users to deploy new policies or services based on new protocols conveniently and rapidly. For
example, carriers can implement security or QoS policies on any video, voice, or P2P protocols easily using
POF.
160