Page 78 - ITU-T Focus Group Digital Financial Services – Technology, innovation and competition
P. 78
ITU-T Focus Group Digital Financial Services
Technology, Innovation and Competition
Appendix B: Identity technologies
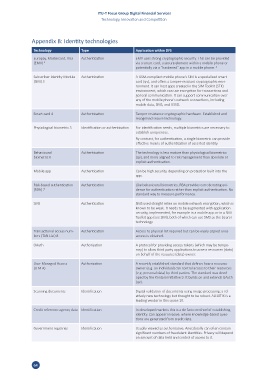
Technology Type Application within DFS
Europay, Mastercard, Visa Authentication EMV uses strong cryptographic security. This can be provided
(EMV) 1 via a smart card, a secure element within a mobile phone or
potentially via a “hardened” app in a mobile phone. 2
Subscriber Identity Module Authentication A GSM-compliant mobile phone’s SIM is a specialised smart
(SIM) 3 card (qv), and offers a tamper-resistant cryptographic envi-
ronment. It can host apps created in the SIM Toolkit (STK)
environment, which can use encryption for transactions and
general communication. It can support communication over
any of the mobile phone’s network connections, including
mobile data, SMS, and USSD.
Smart card 4 Authentication Tamper resistance cryptographic hardware. Established and
recognised secure technology.
Physiological biometric 5 Identification or authentication For identification needs, multiple biometrics are necessary to
establish uniqueness.
By contrast, for authentication, a single biometric can provide
effective means of authentication of asserted identity.
Behavioural Authentication The technology is less mature than physiological biometrics
biometric 6 (qv), and more aligned to risk management than absolute or
explicit authentication.
Mobile app Authentication Can be high security, depending on protection built into the
app.
Risk-based authentication Authentication Like behavioural biometrics, RBA provides corroborating evi-
(RBA) 7 dence for authentication rather than explicit authentication. No
standard way to measure performance.
SMS Authentication SMS used straight relies on mobile network encryption, which is
known to be weak. It needs to be augmented with application
security, implemented, for example in a mobile app or in a SIM
Toolkit app (see SIM), both of which can use SMS as the bearer
technology.
Transactional access num- Authentication Access to physical list required but can be easily copied once
bers (TAN List) 8 access is obtained.
OAuth Authorisation A protocol for providing access tokens (which may be tempo-
rary) to allow third party applications to access resources (data)
on behalf of the resource (data) owner.
User Managed Access Authorisation A recently established standard that defines how a resource
(U M A) owner (e.g. an individual) can control access to their resources
(e.g. personal data) by third parties. The standard was devel-
oped by the Kantara Initiative 9. It builds on and extends OAuth
(qv).
Scanning documents Identification Digital validation of documents using image processing; a rel-
atively new technology but thought to be robust. AU10TIX is a
leading vendor in this space 10.
Credit reference agency data Identification In developed markets this is a de facto method of establishing
identity. Can appear invasive, where knowledge-based ques-
tions are generated from credit data.
Government registries Identification Usually viewed as authoritative. Anecdotally can often contain
significant numbers of fraudulent identities. Privacy will depend
on amount of data held and control of access to it.
64