Page 76 - ITU-T Focus Group Digital Financial Services – Technology, innovation and competition
P. 76
ITU-T Focus Group Digital Financial Services
Technology, Innovation and Competition
A.5.5 Personal IDP model summary
Personal IDP model
Description Involves the use of personal data stores to control the ways in which previously collected
identity attributes are shared.
Strengths • Less susceptible to large scale data breaches;
• Greater control passed on to the individual;
• Privacy enhancing.
Weaknesses • Potential for unrealistic expectation on individual to manage complex range of
data attributes;
• Security of personal data is subject to personal storage device, or cloud
encryption mechanism;
• Business model for this architecture remains yet to be proven.
Examples MyDex, Meeco, Microsoft U-Prove
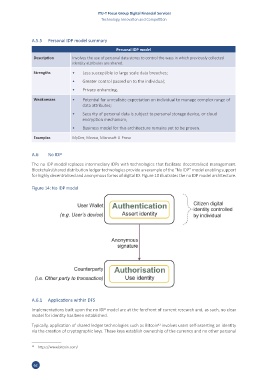
A.6 No IDP
The no IDP model replaces intermediary IDPs with technologies that facilitate decentralised management.
Blockchain/shared distribution ledger technologies provide an example of the “No IDP” model enabling support
for highly decentralised and anonymous forms of digital ID. Figure 10 illustrates the no IDP model architecture.
Figure 14: No IDP model
A.6.1 Applications within DFS
Implementations built upon the no IDP model are at the forefront of current research and, as such, no clear
model for identity has been established.
Typically, application of shared ledger technologies such as Bitcoin involves users self-asserting an identity
42
via the creation of cryptographic keys. These keys establish ownership of the currency and no other personal
42 https:// www. bitcoin. com/
62