Page 567 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 567
Applications 1
7.2 Service roles
There can be various types of service roles, each with differing capabilities. Categorization of each of the
identified service roles facilitates identification of appropriate service capabilities in this Recommendation.
For this purpose, the service roles in the Smart Farming service are categorized in Table 1.
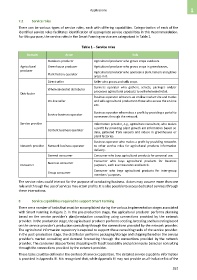
Table 1 – Service roles
Domain Actor Role
Outdoors producer Agricultural producer who grows crops outdoors.
Agricultural Greenhouse producer Agricultural producer who grows crops in greenhouses.
producer Agricultural producer who operates a plant factory and grows
Plant factory operator
crops in it.
Direct seller Seller who grows and sells crops.
Business operator who gathers, selects, packages and/or
Wholesale/retail distributor
Distributor processes agricultural products to sell wholesale/retail.
Business operator who runs an on-line market site and trades
On-line seller and sells agricultural products to those who access the on-line
site.
Business operator who makes a profit by providing a portal to
Service business operator
consumers through the network.
Service provider Information provider, e.g., agriculture consultant, who makes
a profit by providing plant growth aid information based on
Content business operator
data, gathered from sensors and videos in greenhouses or
plant factories.
Business operator who makes a profit by providing networks
Network provider Network business operator to other service roles for agricultural products information
delivery.
General consumer Consumer who buys agricultural products for personal use.
Consumer who buys agricultural products for business
Business consumer
Consumer purposes, such as restaurants and hotels.
Consumer who buys agricultural products for inter-group
Group consumer
members' purposes.
The service roles could interact for the purpose of conducting business. Actors may assume more than one
role and through the use of services may attain profits. It is also possible to access dedicated services through
these interactions.
8 Service capabilities required to support Smart Farming
There are a number of tasks that must be accomplished during the various implementation stages associated
with Smart Farming in Figure 2. In the pre-production stage, the agricultural producer performs planning
based on the service provider's plan/production consulting using connections provided by the network
provider. In the production stage, the agricultural producer performs seeding, breeding and harvesting based
on the service provider's production consulting through the connections provided by the network provider.
The agricultural information repository is required to support these consulting tasks of the service provider.
In the post-production stage, the distributor performs packaging/storage and shipping based on the service
provider's market consulting and demand forecasting through the connections provided by the network
provider. The consumer also performs shopping with food traceability and price inquiry based on consulting
through the connections provided by the network provider.
These tasks could be defined in the context of service capabilities. The detailed service capability information
is provided in Appendix III. It is recognized that, while Appendix III may not provide an all-inclusive list of the
557