Page 549 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 549
Applications 1
A device is a piece of equipment with the mandatory capabilities of communication and optional capabilities
of sensing, actuation, data capture, data storage and data processing. The devices collect various kinds of
information and provide it to the information and communication networks for further processing. Some
devices also execute operations based on information received from the information and communication
networks.
Devices communicate with other devices: they communicate through the communication network via a
gateway (case a), through the communication network without a gateway (case b) or directly, that is without
using the communication network (case c). Also, combinations of cases a and c, and cases b and c are
possible; for example, devices can communicate with other devices using direct communication through a
local network (i.e., a network providing local connectivity between devices and between devices and a
gateway, such as an ad-hoc network) (case c) and then communication through the communication network
via a local network gateway (case a).
NOTE 1 – Although Figure 2 shows only interactions taking place in the physical world (communications between
devices), interactions also take place in the information world (exchanges between virtual things) and between the
physical world and the information world (exchanges between physical things and virtual things).
The IoT applications include various kinds of applications, e.g., "intelligent transportation systems", "smart
grid", "e-health" or "smart home". The applications can be based on proprietary application platforms, but
can also be built upon common service/application support platform(s) providing generic enabling
capabilities, such as authentication, device management, charging and accounting.
The communication networks transfer data captured by devices to applications and other devices, as well as
instructions from applications to devices. The communication networks provide capabilities for reliable and
efficient data transfer. The IoT network infrastructure may be realized via existing networks, such as
conventional TCP/IP-based networks, and/or evolving networks, such as next generation networks (NGN) [b-
ITU-T Y.2001].
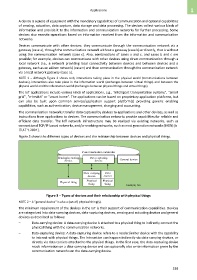
Figure 3 shows the different types of devices and the relationship between devices and physical things.
Communication networks
Sensing/actuating Data capturing
device device General device
Data carrying Data
device carrier
Physical Physical
Physical thing
thing thing
Y.2060(12)_F03
Figure 3 – Types of devices and their relationship with physical things
NOTE 2 – A "general device" is also a (set of) physical thing(s).
The minimum requirement of the devices in the IoT is their support of communication capabilities. Devices
are categorized into data-carrying devices, data-capturing devices, sensing and actuating devices and general
devices as described as follows:
– Data-carrying device: A data-carrying device is attached to a physical thing to indirectly connect the
physical thing with the communication networks.
– Data-capturing device: A data-capturing device refers to a reader/writer device with the capability
to interact with physical things. The interaction can happen indirectly via data-carrying devices, or
directly via data carriers attached to the physical things. In the first case, the data-capturing device
reads information on a data-carrying device and can optionally also write information given by the
communication networks on the data-carrying device.
539