Page 548 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 548
1 Applications
Any TIME communication
- on the move
- night - outdoor
- daytime - indoor (away from the computer)
- at the computer
Any PLACE communication
- between computers
- human to human, not using a computer
- human to thing, using generic equipment
- thing to thing
Any THING communication
Y.2060(12)_F01
Figure 1 – The new dimension introduced in the Internet of things [b-ITU Report]
Regarding the IoT, things are objects of the physical world (physical things) or of the information world
(virtual world) which are capable of being identified and integrated into communication networks. Things
have associated information, which can be static and dynamic.
Physical things exist in the physical world and are capable of being sensed, actuated and connected. Examples
of physical things include the surrounding environment, industrial robots, goods and electrical equipment.
Virtual things exist in the information world and are capable of being stored, processed and accessed.
Examples of virtual things include multimedia content and application software.
6.2 Technical overview of the IoT
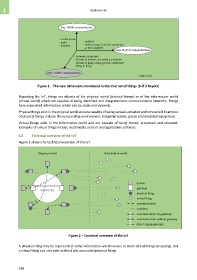
Figure 2 shows the technical overview of the IoT.
Physical world Information world
device
a communication
networks gateway
physical thing
virtual thing
b
c communication
mapping
a communication via gateway
b communication without gateway
c direct communication
Figure 2 – Technical overview of the IoT
A physical thing may be represented in the information world via one or more virtual things (mapping), but
a virtual thing can also exist without any associated physical thing.
538