Page 860 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 860
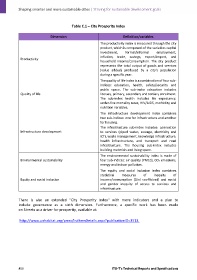
Table C.1 – City Prosperity Index
Dimension Definition/variables
The productivity index is measured through the city
product, which is composed of the variables capital
investment, formal/informal employment,
inflation, trade, savings, export/import, and
Productivity
household income/consumption. The city product
represents the total output of goods and services
(value added) produced by a city's population
during a specific year.
The quality of life index is a combination of four sub‐
indices: education, health, safety/security and
public space. The sub‐index education includes
Quality of life literacy, primary, secondary and tertiary enrolment.
The sub‐index health includes life expectancy,
under‐five mortality rates, HIV/AIDS, morbidity and
nutrition variables.
The infrastructure development index combines
two sub‐indices: one for infrastructure and another
for housing.
The infrastructure sub‐index includes: connection
Infrastructure development to services (piped water, sewage, electricity and
ICT), waste management, knowledge infrastructure,
health infrastructure, and transport and road
infrastructure. The housing sub‐index includes
building materials and living space.
The environmental sustainability index is made of
Environmental sustainability four sub‐indices: air quality (PM10), CO2 emissions,
energy and indoor pollution.
The equity and social inclusion index combines
statistical measures of inequity of
Equity and social inclusion income/consumption (Gini coefficient) and social
and gender inequity of access to services and
infrastructure.
There is also an extended "City Prosperity Index" with more indicators and a plan to
include governance as a sixth dimension. Furthermore, a specific work has been made
on Streets as a driver for prosperity, available at:
http://www.unhabitat.org/pmss/listItemDetails.aspx?publicationID=3513.
850 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications