Page 587 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 587
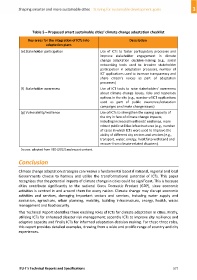
Table 5 – Proposed smart sustainable cities' climate change adaptation checklist
Key areas for the integration of ICTs into Description
adaptation plans
(e) Stakeholder participation Use of ICTs to foster participatory processes and
improve stakeholder engagement in climate
change adaptation decision‐making (e.g., social
networking tools used to broaden stakeholder
participation in adaptation processes, number of
ICT applications used to increase transparency and
share citizen's voices as part of adaptation
processes)
(f) Stakeholder awareness Use of ICT tools to raise stakeholders' awareness
about climate change issues, risks and responses
options in the city (e.g., number of ICT applications
used as part of public awareness/education
campaigns on climate change issues)
(g) Vulnerability/resilience Use of ICTs to strengthen the coping capacity of
the city in face of climate change impacts,
including increased livelihoods' resilience, more
robust public utilities infrastructures (e.g., number
of cases in which ICTs were used to improve the
ability of different city sectors and services (e.g.,
transport, water, energy, health) to withstand and
recover from climate‐related disasters).
Source: adapted from IIED (2012) and report content.
Conclusion
Climate change adaptation strategies can receive a fundamental boost if national, regional and local
Governments choose to harness and utilize the transformational potential of ICTs. This paper
recognizes that the potential impacts of climate change in cities could be significant. This is because
cities contribute significantly to the national Gross Domestic Product (GDP), since economic
activities is centred in and around them for every nation. Climate change may disrupt economic
activities and services, damaging important sectors and services, including water supply and
sanitation, agriculture, urban planning, mobility, building infrastructure, energy, health, waste
management and food security.
This Technical Report identifies three enabling roles of ICTs for climate adaptation in cities. Firstly,
utilizing ICTs for enhanced disaster risk management; secondly ICTs to improve city resilience and
adaptive capacity and finally ICTs for informed adaptation decision making. For these three roles,
this report provides detailed examples, drawing from a wide and prolific range of country and city
experiences.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 577