Page 586 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 586
Having suggested a framework for city mayors to integrate ICTs in their climate change adaptations
plans and help to build their cities' resilience, this section provides a checklist that can support the
assessment of their ICT‐enabled adaptation plans. This checklist can help mayors and municipal
authorities to evaluate whether climate change adaptation actions were successful and if ICTs met
their role of enablers in the process.
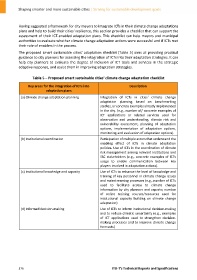
The proposed smart sustainable cities' adaptation checklist (Table 5) aims at providing practical
guidance to city planners for assessing the integration of ICTs into their adaptation strategies. It can
help city planners to evaluate the degree of inclusion of ICT tools and services in the strategic
adaptive response, and assist them in improving adaptation strategies.
Table 5 – Proposed smart sustainable cities' climate change adaptation checklist
Key areas for the integration of ICTs into Description
adaptation plans
(a) Climate change adaptation planning Integration of ICTs in cities' climate change
adaptation planning based on benchmarking
studies, or concrete examples already implemented
in the city. (e.g., number of/ concrete examples of
ICT applications or related services used for
observation and understanding, climate risk and
vulnerability assessment, planning of adaptation
options, implementation of adaptation options,
monitoring and evaluation of adaptation options).
(b) Institutional coordination Participation of multiple actors that understand the
enabling effect of ICTs in climate adaptation
policies. Use of ICTs in the coordination of climate
risk management among relevant institutions and
SSC stakeholders (e.g., concrete examples of ICTs
usage to enable communication between key
players involved in adaptation actions).
(c) Institutional knowledge and capacity Use of ICTs to enhance the level of knowledge and
training of key personnel in climate change issues
and mainstreaming processes (e.g., number of ICTs
used to facilitate access to climate change
information by city planners and experts; number
of online training courses/resources used for
institutional capacity building on climate change
adaptation)
(d) Informed decision‐making Use of ICTs to inform institutional decision‐making
and to reduce climatic uncertainty (e.g., examples
of ICT applications used to strengthen decision‐
making processes and to improve climate change
forecasts)
576 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications