Page 571 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 571
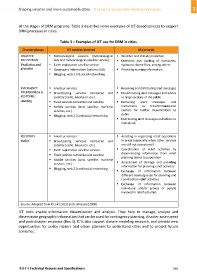
all the stages of DRM programs. Table 3 describes some examples of ICT‐based services to support
DRM processes in cities.
Table 3 – Examples of ICT use for DRM in cities
Disaster phases ICT services involved Major tasks
DISASTER Meteorological services (meteorological Weather and climate prediction
PREVENTION: aids and meteorological‐satellite service) Detection and tracking of hurricanes,
Prediction and Earth exploration‐satellite service typhoons, forest fires, among others
detection Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Providing warning information
Blogging, web 2.0 & social networking
EMERGENCY Amateur services Receiving and distributing alert messages
PREPARDNESS & Broadcasting services terrestrial and Disseminating alert messages and advice
RESPONSE: satellite (radio, television, etc.) to large sections of the public
Alerting Fixed services terrestrial and satellite Delivering alert messages and
Mobile services (land, satellite, maritime instructions to telecommunication
services, etc.) centers for further dissemination to
public
Blogging, web 2.0 and social networking
Distributing alert messages and advice to
individuals
RECOVERY: Amateur services Assisting in organizing relief operations
Relief Broadcasting services terrestrial and in areas (especially when other services
satellite (radio, television, etc.) are still not operational)
Earth exploration‐satellite services Coordination of relief activities by
disseminating information from relief
Fixed services terrestrial and satellite
planning teams to population
Mobile services (land, satellite, maritime
services, etc.) Assessment of damage and providing
information for planning relief activities
Blogging, web 2.0 and social networking
Exchange of information between
different teams/groups for planning and
coordination relief activities
Exchange of information between
individuals and/or groups of people
involved in relief activities
Source: Adapted from ITU‐R (2013) and LIRNEasia (2008)
ICT tools enable information dissemination and analysis. They help to manage, analyze and
disseminate geographic information that can be used for contingency planning, disaster assessment
and post‐disaster response (Box 4). ICTs also support climate modeling research, and provide new
opportunities for policy makers and urban planners to understand cities and to project future
scenarios.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 561