Page 325 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 325
The SMART system also allows the creation of polygons that are targeted toward specific geographic
areas of interest within which one wants to disseminate alerts. This definition is made from
geo‐referenced graphical interface. To this end, SMART has an updated database of the location of
cell phone stations BSC / RNC and BTS / NodeB that automatically updates through the CBC (Cell
Broadcast Center) that becomes the interface from the network mobile phone.
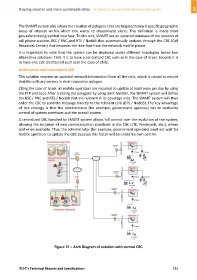
It is important to note that the system can be deployed under different topologies hence two
alternative solutions. First, it is to have a centralized CBC such as in the case of Israel. Second, it is
to have one CBC distributed such as in the case of Chile.
Architecture with centralized CBC
This solution requires an updated network information from all the cells, which is crucial to ensure
that the cells are correct in their respective polygon.
Citing the case of Israel, all mobile operators are required to update at least once per day by using
the FTP protocol. After creating the polygons by using alert handler, the SMART system will define
the BSC / RNC and BTS / NodeB that are relevant in its coverage area. The SMART system will then
order the CBC to send the message directly to the relevant cells (BTS / NodeB). The key advantage
of this strategy is that the administrator (for example, government agencies) has to centralize
control of system interfaces and the overall system.
A centralized CBC handled by SMART system allows full control over the evolution of the system,
allowing the inclusion of new communication standards in the CBC (LTE, femtocells, etc.), where
and when available. Thus, the administrator (for example, government agencies) need not wait for
mobile operators to update the CBC because this factor will be under his own control.
Figure 74 – Arch Diagram of solution with central CBC
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 315