Page 170 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 170
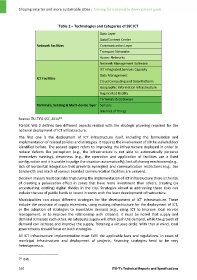
Table 2 – Technologies and Categories of SSC ICT
Data Layer
Data/Content Center
Network Facilities Communication Layer
Transport Networks
Access Networks
Network Management Software
ICT Integrated Services Capacity
Data Management
ICT Facilities
Cloud Computing and Data Platform
Geographic Information Infrastructure
Augmented Reality
Terminals & Gateways
Terminals, Sensing & Multi‐device layer Sensors
Internet of Things
14
Source: ITU‐T FG‐SSC, 2014
FG‐SSC WG 2 defines two different aspects related with the strategic planning required for the
national deployment of ICT infrastructure.
The first one is the deployment of ICT infrastructure itself, including the formulation and
implementation of related policies and strategies. It requires the involvement of all the stakeholders
identified before. The second aspect refers to improving the infrastructure deployed in order to
reduce defects like perception (e.g., the infrastructure is not able to automatically perceive
themselves running), cleverness (e.g., the operation and application of facilities use a fixed
configuration and it is unable to judge the situation automatically), lack of sharing mechanisms(e.g.,
lack of horizontal integration that prevents synergies) and communication restrictions (e.g., the
bandwidth and reach of various branded communication facilities are uneven).
Decision makers must consider that during the implementation of ICT infrastructure there is the risk
of creating a polarization effect in zones that have more investment than others, creating (or
accentuating existing) digital divides in the city. Strategies aimed at addressing these risks can
include the use of public funds to invest in zones with the least development infrastructure.
Municipalities can adopt different strategies for the development of ICT infrastructure. These
include the provision of supply incentives, using existing infrastructure for the deployment of ICT,
or the adoption of strategies to incentivize demand (e.g., using ICT to improve local service
management, or to improve the relationship with citizens). It must be noted that supply and
demand stimulate each other. An adequate supply will often push the demand, while the growth of
demand can increase and improve the supply, fostering a virtuous circle. With that in mind, local
governments should focus on both strategies.
All ICT infrastructure implementation must fulfil the applicable laws and regulations. In cases of
municipal infrastructure and deployment of projects, financing strategies tend to be very
heterogeneous.
____________________
14 Ibid.
160 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications