Page 165 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 165
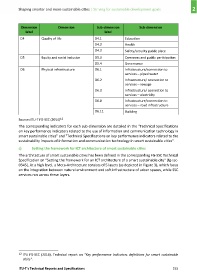
Dimension Dimension Sub‐dimension Sub‐dimension
label label
D4 Quality of life D4.1 Education
D4.2 Health
D4.3 Safety/security public place
D5 Equity and social inclusion D5.3 Openness and public participation
D5.4 Governance
D6 Physical infrastructure D6.1 Infrastructure/connection to
services – piped water
D6.2 Infrastructure/ connection to
services – sewage
D6.3 Infrastructure/ connection to
services – electricity
D6.8 Infrastructure/connection to
services – road infrastructure
D6.11 Building
12
Source: ITU‐T FG‐SSC (2014)
The corresponding indicators for each sub‐dimension are detailed in the "Technical Specifications
on key performance indicators related to the use of information and communication technology in
smart sustainable cities" and "Technical Specifications on key performance indicators related to the
sustainability impacts of information and communication technology in smart sustainable cities".
c) Setting the framework for ICT architecture of smart sustainable cities
The architecture of smart sustainable cities has been defined in the corresponding FG‐SSC Technical
Specification on “Setting the framework for an ICT architecture of a smart sustainable city” (fg‐ssc‐
0345), At a high level, a Meta‐Architecture consists of 5 layers (as depicted in Figure 3), which focus
on the integration between natural environment and soft infrastructure of urban spaces, while SSC
services run across these layers.
____________________
12 ITU FG‐SSC (2014), Technical report on "Key performance indicators definitions for smart sustainable
cities".
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 155