Page 121 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 121
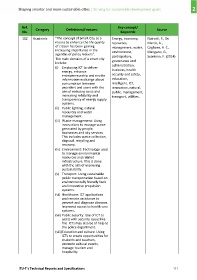
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
112 Academic "The concept of Smart City as a Energy, economy, Neirotti, P., De
means to enhance the life quality resources, Marco, A.,
of citizen has been gaining management, water, Cagliano, A. C.,
increasing importance in the environment, Mangano, G.,
agendas of policy makers".
participatory, Scorrano, F. (2014)
The main domains of a smart city governance and
include:
administration,
(i) Employing ICT to deliver
energy, enhance business, health
entrepreneurship and enable security and safety,
information exchange about education,
consumption between intelligent, ICT,
providers and users with the innovation, natural,
aim of reducing costs and public, management,
increasing reliability and transport, utilities.
transparency of energy supply
systems.
(ii) Public lighting, natural
resources and water
management.
(iii) Waste management: Using
innovations to manage waste
generated by people,
businesses and city services.
This includes waste collection,
disposal, recycling and
recovery.
(iv) Environment: Technology used
to manage environmental
resources and related
infrastructure. This is done
with the aim of improving
sustainability.
(v) Transport: Using sustainable
public transportation based on
environmentally friendly fuels
and innovative propulsion
systems.
(vi) Healthcare: ICT applications
and remote assistance to
prevent and diagnose diseases.
Improved access to health care
systems.
(vii) Public security: Use of ICT to
assist with security issues like
fire. ICTs may also be of help to
the police department.
(viii) Education and culture: Using
ICTs to create opportunities for
students and teachers,
promote cultural events,
manage tourism and
hospitality.
ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications 111