Page 122 - Shaping smarter and more sustainable cities - Striving for sustainable development goals
P. 122
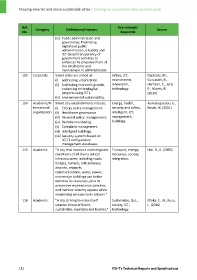
Ref. Category Definitions/Features Key concept/ Source
No. Keywords
(ix) Public administration and
governance: Promoting
digitalized public
administration, e‐ballots and
ICT‐based transparency of
government activities to
enhance the empowerment of
the inhabitants and
involvement in administration.
113 Corporate Smart cities are aimed at: Urban, ICT, Naphade, M.,
(i) addressing urbanization. environment, Guruduth, B.,
(ii) facilitating economic growth, innovation, Harrison, C., Jurij,
enhancing technological technology. P., Morris, R.
progress using ICTs. (2014)
(iii) environmental sustainability.
114 Academic/In Smart city establishments include: Energy, health, Asimakopoulou, E.,
ternational (i) Energy policy management. security and safety, Bessis, N. (2011)
organization (ii) Healthcare governance. intelligent, ICT,
(iii) Financial policy management. management,
(iv) Remote monitoring. buildings.
(v) Complaint management.
(vi) Intelligent buildings.
(vii) Security systems based on
ICT,IT configuration
management databases.
115 Academic "A city that monitors and integrates Transport, energy, Hall, R., E. (2000)
conditions of all the its critical resources, society,
infrastructures, including roads, integration.
bridges, tunnels, rails subways,
airports, seaports,
communications, water, power,
even major buildings can better
optimize its resources, plan its
preventive maintenance activities,
and monitor security aspects while
maximizing services to its citizens."
116 Academic "A city striving to make itself Sustainable, QoL, Nfuka, E., N., Rusu,
smarter (more efficient, society, ICT, L. (2010)
sustainable, equitable and livable)." technology.
112 ITU‐T's Technical Reports and Specifications