Page 425 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 425
Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things 4
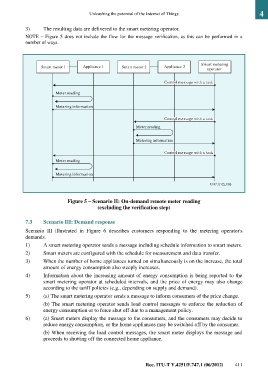
3) The resulting data are delivered to the smart metering operator.
NOTE – Figure 5 does not include the flow for the message verification, as this can be performed in a
number of ways.
Smart metering
Smart meter 1 Appliance 1 Smart meter 2 Appliance 2
operator
Control message with a task
Meter reading
Metering information
Control message with a task
Meter reading
Metering information
Control message with a task
Meter reading
Metering information
F .747.1(12)_F05
Figure 5 – Scenario II: On-demand remote meter reading
(excluding the verification step)
7.3 Scenario III: Demand response
Scenario III illustrated in Figure 6 describes customers responding to the metering operator's
demands.
1) A smart metering operator sends a message including schedule information to smart meters.
2) Smart meters are configured with the schedule for measurement and data transfer.
3) When the number of home appliances turned on simultaneously is on the increase, the total
amount of energy consumption also steeply increases.
4) Information about the increasing amount of energy consumption is being reported to the
smart metering operator at scheduled intervals, and the price of energy may also change
according to the tariff policies (e.g., depending on supply and demand).
5) (a) The smart metering operator sends a message to inform consumers of the price change.
(b) The smart metering operator sends load control messages to enforce the reduction of
energy consumption or to force shut off due to a management policy.
6) (a) Smart meters display the message to the consumers, and the consumers may decide to
reduce energy consumption, or the home appliances may be switched off by the consumer.
(b) When receiving the load control messages, the smart meter displays the message and
proceeds to shutting off the connected home appliance.
Rec. ITU-T Y.4251/F.747.1 (06/2012) 411