Page 422 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 422
4 Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things
6.2 Technical overview of smart metering
It is not only governments and utility companies, such as electricity, gas and water suppliers, but
also researchers, that have been interested in automatic meter reading based on communication
systems. Examples of smart metering benefits to customers, governments and utility companies are:
– lower metering cost
– energy savings for residential consumers
– reliability of supply
– various pricing schemes to attract new costumers
– easier detection of fraud and of outages
– automated billing.
Smart metering comprises metering and exchange of meter information between smart meters and
utility companies. Various technologies can be used for metering and exchanging meter
information. For example, power-line communications have been used for delivering electricity
power to consumers and for transmitting gas and water measurements to utility providers.
Alternatively, mobile networks can be used for exchanging messages in an automatic meter reading
system.
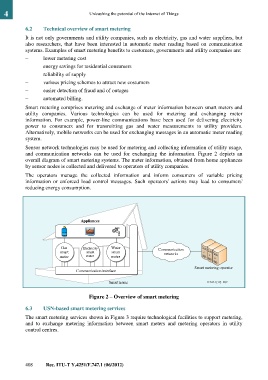
Sensor network technologies may be used for metering and collecting information of utility usage,
and communication networks can be used for exchanging the information. Figure 2 depicts an
overall diagram of smart metering systems. The meter information, obtained from home appliances
by sensor nodes is collected and delivered to operators of utility companies.
The operators manage the collected information and inform consumers of variable pricing
information or enforced load control messages. Such operators' actions may lead to consumers'
reducing energy consumption.
Appliances
Gas Electricity Water Communication
smart smart smart networks
meter meter meter
Smart metering operator
Communication interface
Smart home F.747.1(12)_F02
Figure 2 – Overview of smart metering
6.3 USN-based smart metering services
The smart metering services shown in Figure 3 require technological facilities to support metering,
and to exchange metering information between smart meters and metering operators in utility
control centres.
408 Rec. ITU-T Y.4251/F.747.1 (06/2012)