Page 424 - Unleashing the potenti al of the Internet of Things
P. 424
4 Unleashing the potential of the Internet of Things
7 Smart metering service scenarios
The following scenarios illustrate the use of smart metering services.
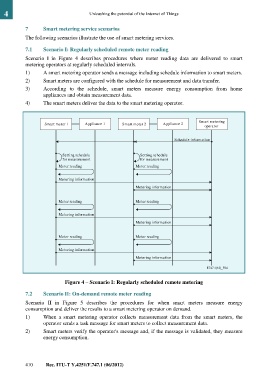
7.1 Scenario I: Regularly scheduled remote meter reading
Scenario I in Figure 4 describes procedures where meter reading data are delivered to smart
metering operators at regularly scheduled intervals.
1) A smart metering operator sends a message including schedule information to smart meters.
2) Smart meters are configured with the schedule for measurement and data transfer.
3) According to the schedule, smart meters measure energy consumption from home
appliances and obtain measurement data.
4) The smart meters deliver the data to the smart metering operator.
Smart metering
Smart meter 1 Appliance 1 Smart meter 2 Appliance 2
operator
Schedule information
Setting schedule Setting schedule
for measurement for measurement
Meter reading Meter reading
Metering information
Metering information
Meter reading Meter reading
Metering information
Metering information
Meter reading Meter reading
Metering information
Metering information
F.747.1(12)_F04
Figure 4 – Scenario I: Regularly scheduled remote metering
7.2 Scenario II: On-demand remote meter reading
Scenario II in Figure 5 describes the procedures for when smart meters measure energy
consumption and deliver the results to a smart metering operator on demand.
1) When a smart metering operator collects measurement data from the smart meters, the
operator sends a task message for smart meters to collect measurement data.
2) Smart meters verify the operator's message and, if the message is validated, they measure
energy consumption.
410 Rec. ITU-T Y.4251/F.747.1 (06/2012)