Page 101 - Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities: The Case of Dubai
P. 101
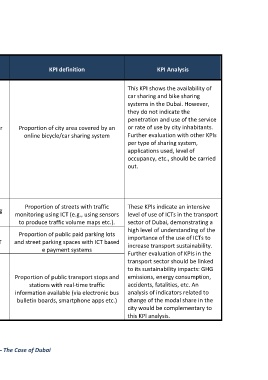
I: Core KPI
Sub-dimension o Indicator KPI definition KPI Analysis
A: Additional N
This KPI shows the availability of
car sharing and bike sharing
systems in the Dubai. However,
they do not indicate the
penetration and use of the service
Availability of online bicycle/car Proportion of city area covered by an or rate of use by city inhabitants.
A 682
sharing system online bicycle/car sharing system Further evaluation with other KPIs
per type of sharing system,
applications used, level of
occupancy, etc., should be carried
out.
D6.8 Infrastructure/
connection to services
– road Availability of traffic monitoring Proportion of streets with traffic These KPIs indicate an intensive
I 681 monitoring using ICT (e.g., using sensors level of use of ICTs in the transport
using ICT
to produce traffic volume maps etc.). sector of Dubai, demonstrating a
high level of understanding of the
Proportion of public paid parking lots importance of the use of ICTs to
I 682 Availability of parking using ICT and street parking spaces with ICT based increase transport sustainability.
e payment systems
Further evaluation of KPIs in the
transport sector should be linked
to its sustainability impacts: GHG
Proportion of public transport stops and emissions, energy consumption,
Availability of real-time traffic stations with real-time traffic accidents, fatalities, etc. An
I 683
information information available (via electronic bus analysis of indicators related to
bulletin boards, smartphone apps etc.) change of the modal share in the
city would be complementary to
this KPI analysis.
71 Implementing ITU-T International Standards to Shape Smart Sustainable Cities – The Case of Dubai