Page 96 - Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016
P. 96
risk that speculative investments will not be repaid The most ambitious smart city projects, such
as quickly as expected . as India’s project to create 100 smart cities, are
43
spending hundreds of millions of dollars to build
more liveable and sustainable communities . To
44
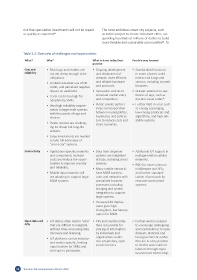
Table 3.2: Overview of challenges and opportunities
What? Why? What is done today/best Possible way forward
practice
Cost and • Most tags and readers are • Ongoing development • Standardized functions
reliability not yet cheap enough to be and deployment of in smart phones could
ubiquitous. cheaper, more efficient interact with tags and
• Limited consumer use of QR and reliable hardware sensors, including via web
codes, and perceived negative and protocols. browsers.
impact on aesthetics. • Innovation centres to • Greater attention to aes-
• Costs can be too high for stimulate market entry thetics of tags, such as
35
adoption by SMEs. and competition. dot-less visual codes .
• Very high reliability require- • Public-private partner- • Further R&D in areas such
ments in large-scale systems ships and cooperation as energy scavenging,
with thousands of tags and between municipalities, low-energy protocols and
devices. businesses and contrac- algorithms, and high-reli-
• Power sources are challeng- tors to reduce costs and ability systems.
share resources.
ing for cheap but long-life
sensors.
• Large investments are needed
to take full advantage of
“smart city” systems.
Connectivity • Application-specific networks • Data from disparate • Additional IoT support in
and components increase systems are integrated next-generation cellular
costs and reduce the oppor- at hubs, including cloud networks.
tunities to improve security services. • R&D for more common
and reliability. • Many mobile networks middleware and APIs,
• Mobile data networks still have M2M business and further standard-
are adapting to support large units and networks with ization of protocols for
M2M systems. specialized business resource-constrained
processes, including systems.
charging and system
integration to support
large systems.
• Increased 4G deploy-
ment gives high
throughput, low latency
option for M2M.
Open data and • IoT data is often held in “silos” • City and country initia- • Further work is needed
APIs that are difficult to integrate tives can provide for to encourage cataloguing
without time-consuming data sharing of information and contributions to open
discovery and licensing. by individuals and datasets. National and
• IoT platforms can be industry- organizations under local government author-
and vendor-specific, limiting non-proprietary, open- ities are in a key position
opportunities for SMEs and source licences. to do this and could col-
start-ups to participate. laborate through Open
Government Partnership.
78 Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016