Page 56 - Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016
P. 56
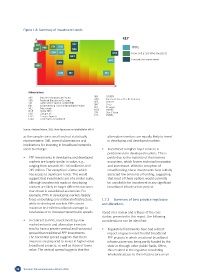
Figure 1.8: Summary of investment trends
KEY
SHY STA GUS MIP
HIP PEB NBS PPPs
COM SIG QNB New and alternative investors
MET
APG Innovative investments
JBN
MEX
GUG NIC SEA
Abbreviations
MIP Mobile Infrastructure Project SIG SIGFOX
NBS National Boradband Scheme APG Facebook Asian-Pacific Gateway
NIC national ICT Backbone (NICTBB) SEA Seacom
JBN Johannesburg National Broadband Project SHY Shyp
MLi Metroweb HIP Hipcom
QNR Qatar NRN MEX meXBT
GUS Google US STA Star Citizen
GUG Google Uganda PEB Pebble
COM Community broadband
Source: Analysys Mason, 2015. Note figures are not abailable for MGTS
as the sample size is small and not statistically alternative investors are equally likely to invest
representative. Still, several observations and in developing and developed markets.
implications for investing in broadband networks
seem to emerge: • Investment in higher-layer services is
predominant in developed markets. This is
• PPP investments in developing and developed partly due to the maturity of the Internet
markets are largely similar in value, e.g., ecosystem, which fosters technical innovation
ranging from around USD 100 million to USD and investment. With the exception of
245 million. The exception is Qatar, which crowdfunding, these investments have initially
has access to significant funds. This would attracted low amounts of funding, suggesting
suggest that investments are of a similar scale, that most of these options would currently
although investments made in developing be unsuitable for investment in any significant
markets are likely to target different outcomes broadband infrastructure project.
than those in established economies. For
example, PPPs in developing markets largely
focus on building core national infrastructure, 1.7.2 Summary of best practice regulatory
while in developed markets PPPs aim to considerations
maximize last-mile broadband coverage to
rural areas or to increase transmission speeds. Based on a review and critique of the case
studies presented in this report, the following
• In contrast to PPPs, investments by new considerations can be identified:
market entrants and alternative investors
tend to have a greater vertical and horizontal • Regulatory frameworks have had a direct
spread than traditional PPP investments. impact on government-funded broadband
The horizontal spread suggests that these PPP projects in which a national broadband
investors are prepared to invest in higher-value infrastructure was being partly funded by the
broadband projects, as well as those of lower state or through other public funds. Often,
value. The vertical spread suggests that the this resulted in the regulator mandating
wholesale access to the infrastructure on an
38 Trends in Telecommunication Reform 2016