Page 46 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2024
P. 46
2024 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
constant changes. Configuration items belonging to different proposed inspection method in real-world applications,
models contain different detailed fields, which also evolve demonstrating significant improvements in data quality and
based on business requirements. (2) Heterogeneous CMDB system performance. Finally, the conclusion summarizes the
Data Sources: CMDB configuration item data comes from strengths and limitations of the proposed inspection method
various provincial companies and regional resource pools. and outlines potential directions for future research. In
While there are clear reporting standards, these standards summary, this paper contributes to the field of automated
only apply to coarse-grained validations of field types, O&M by addressing the data issues in CMDB through a
lengths, non-emptiness, etc. Concerning the content of the dynamic and automated inspection system, ensuring higher
fields themselves, logical relationships between fields cannot accuracy, efficiency, and universality in compliance checks.
be verified. (3) Migration of Data from Old Management
Systems: A portion of the data in the CMDB system is 2. METHODOLOGY
migrated from old management systems, and this data
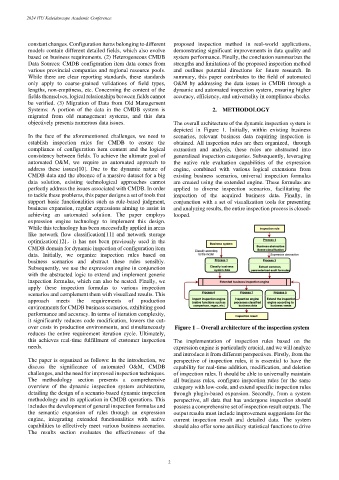
objectively presents numerous data issues. The overall architecture of the dynamic inspection system is
depicted in Figure 1. Initially, within existing business
In the face of the aforementioned challenges, we need to scenarios, relevant business data requiring inspection is
establish inspection rules for CMDB to ensure the obtained. All inspection rules are then organized, through
compliance of configuration item content and the logical extraction and analysis, these rules are abstracted into
consistency between fields. To achieve the ultimate goal of generalized inspection categories. Subsequently, leveraging
automated O&M, we require an automated approach to the native rule evaluation capabilities of the expression
address these issues[10]. Due to the dynamic nature of engine, combined with various logical extensions from
CMDB data and the absence of a massive dataset for a big existing business scenarios, universal inspection formulas
data solution, existing technological approaches cannot are created using the extended engine. These formulas are
perfectly address the issues associated with CMDB. In order applied to diverse inspection scenarios, facilitating the
to tackle these problems, this paper designs a set of tools that inspection of the acquired business data. Finally, in
support basic functionalities such as rule-based judgment, conjunction with a set of visualization tools for presenting
business expansion, regular expressions aiming to assist in and analyzing results, the entire inspection process is closed-
achieving an automated solution. The paper employs looped.
expression engine technology to implement this design.
While this technology has been successfully applied in areas
like network flow classification[11] and network storage
optimization[12],it has not been previously used in the
CMDB domain for dynamic inspection of configuration item
data. Initially, we organize inspection rules based on
business scenarios and abstract these rules sensibly.
Subsequently, we use the expression engine in conjunction
with the abstracted logic to extend and implement generic
inspection formulas, which can also be nested. Finally, we
apply these inspection formulas to various inspection
scenarios and complement them with visualized results. This
approach meets the requirements of production
environments for CMDB business scenarios, exhibiting good
performance and accuracy. In terms of iteration complexity,
it significantly reduces code modification, lowers the cut-
over costs in production environments, and simultaneously Figure 1 – Overall architecture of the inspection system
reduces the entire requirement iteration cycle. Ultimately,
this achieves real-time fulfillment of customer inspection The implementation of inspection rules based on the
needs. expression engine is particularly crucial, and we will analyze
and introduce it from different perspectives. Firstly, from the
The paper is organized as follows: In the introduction, we perspective of inspection rules, it is essential to have the
discuss the significance of automated O&M, CMDB capability for real-time addition, modification, and deletion
challenges, and the need for improved inspection techniques. of inspection rules. It should be able to universally maintain
The methodology section presents a comprehensive all business rules, configure inspection rules for the same
overview of the dynamic inspection system architecture, category with low-code, and extend specific inspection rules
detailing the design of a scenario-based dynamic inspection through plugin-based expansion. Secondly, from a system
methodology and its application in CMDB operations. This perspective, all data that has undergone inspection should
includes the development of general inspection formulas and possess a comprehensive set of inspection result outputs. The
the semantic expansion of rules through an expression output results must include improvement suggestions for the
engine, integrating extended functionalities with native current inspection result and detailed data. The system
capabilities to effectively meet various business scenarios. should also offer some auxiliary statistical functions to drive
The results section evaluates the effectiveness of the
– 2 –