Page 53 - AI Ready – Analysis Towards a Standardized Readiness Framework
P. 53
AI Ready – Analysis Towards a Standardized Readiness Framework
(continued)
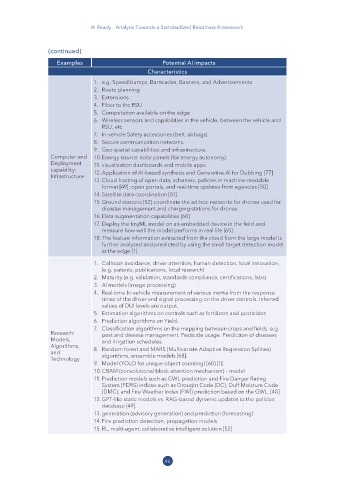
Examples Potential AI impacts
Characteristics
1. e.g. Speed bumps, Barricades, Banners, and Advertisements
2. Route planning
3. Extensions
4. Fiber to the RSU
5. Computation available on the edge
6. Wireless sensors and capabilities in the vehicle, between the vehicle and
RSU, etc
7. In-vehicle Safety accessories (belt, airbags)
8. Secure communication networks.
9. Geo spatial capabilities and infrastructure.
Computer and 10. Energy source: solar panels (for energy autonomy).
Deployment 11. visualization dashboards and mobile apps
capability: 12. Application of AI-based synthesis and Generative AI for Dubbing [77]
Infrastructure
13. Cloud hosting of open data, schemes, policies in machine-readable
format [49], open portals, and real-time updates from agencies [50]
14. Satellite data coordination [51]
15. Ground stations [52] coordinate the ad-hoc networks for drones used for
disaster management and charging stations for drones.
16. Data augmentation capabilities [60]
17. Deploy the tinyML model on an embedded device in the field and
measure how well the model performs in real life [65]
18. The feature information extracted from the cloud from the large model is
further analyzed and predicted by using the small target detection model
at the edge [1]
1. Collision avoidance, driver attention, human detection, local innovation,
(e.g. patents, publications, local research)
2. Maturity (e.g. validation, standards compliance, certifications, labs)
3. AI models (image processing)
4. Real-time In-vehicle measurement of various inertia from the response
times of the driver and signal processing on the driver controls. Inferred
values of DUI levels are output.
5. Estimation algorithms on controls such as fertilizers and pesticides
6. Prediction algorithms on Yield.
7. Classification algorithms on the mapping between crops and fields. e.g.
Research: pest and disease management. Pesticide usage. Prediction of diseases
Models, and irrigation schedules.
Algorithms,
and 8. Random forest and MARS (Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines)
algorithms, ensemble models [68].
Technology
9. Model (YOLO for unique object counting) [60] [1]
10. CBAM (convolutional block attention mechanism) – model
11. Prediction models such as GWL prediction and Fire Danger Rating
System (FDRS) indices such as Drought Code (DC), Duff Moisture Code
(DMC), and Fire Weather Index (FWI) prediction based on the GWL. [48]
12. GPT-like static models vs. RAG-based dynamic updates to the policies
database [49].
13. generation (advisory generation) and prediction (forecasting)
14. Fire prediction detection, propagation models
15. RL, multi-agent, collaborative intelligent solution [52]
46