Page 495 - Cloud computing: From paradigm to operation
P. 495
Cloud Computing management 2
Appendix II
Multi-cloud end to end service management
(This appendix does not form an integral part of this Recommendation.)
The following use case describes the challenges associated with multi-cloud end to end service management.
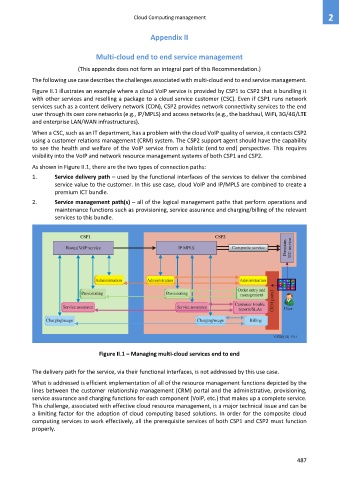
Figure II.1 illustrates an example where a cloud VoIP service is provided by CSP1 to CSP2 that is bundling it
with other services and reselling a package to a cloud service customer (CSC). Even if CSP1 runs network
services such as a content delivery network (CDN), CSP2 provides network connectivity services to the end
user through its own core networks (e.g., IP/MPLS) and access networks (e.g., the backhaul, WiFi, 3G/4G/LTE
and enterprise LAN/WAN infrastructures).
When a CSC, such as an IT department, has a problem with the cloud VoIP quality of service, it contacts CSP2
using a customer relations management (CRM) system. The CSP2 support agent should have the capability
to see the health and welfare of the VoIP service from a holistic (end to end) perspective. This requires
visibility into the VoIP and network resource management systems of both CSP1 and CSP2.
As shown in Figure II.1, there are the two types of connection paths:
1. Service delivery path – used by the functional interfaces of the services to deliver the combined
service value to the customer. In this use case, cloud VoIP and IP/MPLS are combined to create a
premium ICT bundle.
2. Service management path(s) – all of the logical management paths that perform operations and
maintenance functions such as provisioning, service assurance and charging/billing of the relevant
services to this bundle.
CSP1 CSP2
Hosted VoIP service IP MPLS Composite service Premium UC service
Administration Administration Administration
Order entry and
Provisioning Provisioning management
Customer trouble CRM portal
Service assurance Service assurance
reports/SLAs User
Charging/usage Charging/usage Billing
Y.3520(13)_FII.1
Figure II.1 – Managing multi-cloud services end to end
The delivery path for the service, via their functional interfaces, is not addressed by this use case.
What is addressed is efficient implementation of all of the resource management functions depicted by the
lines between the customer relationship management (CRM) portal and the administrative, provisioning,
service assurance and charging functions for each component (VoIP, etc.) that makes up a complete service.
This challenge, associated with effective cloud resource management, is a major technical issue and can be
a limiting factor for the adoption of cloud computing based solutions. In order for the composite cloud
computing services to work effectively, all the prerequisite services of both CSP1 and CSP2 must function
properly.
487