Page 1323 - 5G Basics - Core Network Aspects
P. 1323
Transport aspects 2
6 Introduction and applications
A FlexO (Flexible OTN) group is defined for interoperable interfacing applications. It complements B100G
(beyond 100G) [ITU-T G.709] Edition 5, by providing an interoperable interface for OTUCn transport signals.
The FlexO group interface provides modularity by bonding standard-rate interfaces (e.g., m * 100G), over
which the OTUCn (n ≥ 1) signal is adapted. The value of m is not standardized. The specification of OTUCn in
[ITU-T G.709] excludes interface specific functions such as FEC, scrambling, and bit alignment. The FlexO
interface wraps OTUCn, abstracting the transport signal from the interface. FlexO enables ODUflex services
>100Gbit/s to be supported across multiple interfaces, ahead of next-gen interface standards (e.g., 400GE
[b-IEEE 802.3bs]).
FlexO provides OTN interfaces with comparable functionality as to what was introduced in [OIF FlexE IA] for
Ethernet interfaces.
6.1 FlexO considerations
The considerations and capabilities for a FlexO group:
– provides an interoperable system interface for OTUCn transport signals;
– enables higher capacity ODUflex and OTUCn, by means of bonding m standard-rate interfaces;
– provides interface rate modularity and flexibility;
– provides a frame, alignment, deskew, group management, management communication channel,
and such functions that are not associated with the OTUCn transport signal; and
– reuses 100G modules (e.g., CFP2, QSFP28) by matching the interface rate to OTU4 as specified in
[ITU-T G.709]
The FlexO interface is specified in this recommendation at the external reference point. The logical signal
format FOIC can be reused on a system internal interface. These requirements and the optimizations to the
FlexO groups (e.g., lower latency by removing FEC) are beyond the scope of this recommendation and
covered in [b-ITU-T G-Sup.58].
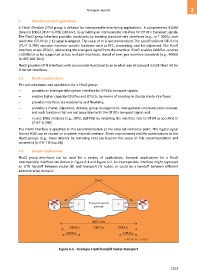
6.2 Sample applications
FlexO group interfaces can be used for a variety of applications. Example applications for a FlexO
interoperable interface are shown in Figure 6-1 and Figure 6-2. An interoperable interface might represent
an OTN handoff between router (R) and transport (T) nodes, or could be a handoff between different
administrative domains.
Figure 6-1 – Example FlexO handoff router-transport
1313