Page 58 - U4SSC KPIs Verification Manual - A guide for verifiers
P. 58
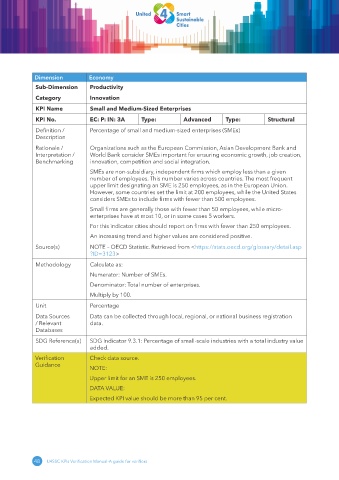
Dimension Economy
Sub-Dimension Productivity
Category Innovation
KPI Name Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
KPI No. EC: P: IN: 3A Type: Advanced Type: Structural
Definition / Percentage of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
Description
Rationale / Organizations such as the European Commission, Asian Development Bank and
Interpretation / World Bank consider SMEs important for ensuring economic growth, job creation,
Benchmarking innovation, competition and social integration.
SMEs are non-subsidiary, independent firms which employ less than a given
number of employees. This number varies across countries. The most frequent
upper limit designating an SME is 250 employees, as in the European Union.
However, some countries set the limit at 200 employees, while the United States
considers SMEs to include firms with fewer than 500 employees.
Small firms are generally those with fewer than 50 employees, while micro-
enterprises have at most 10, or in some cases 5 workers.
For this indicator cities should report on firms with fewer than 250 employees.
An increasing trend and higher values are considered positive.
Source(s) NOTE – OECD Statistic. Retrieved from <https:// stats .oecd .org/ glossary/ detail .asp
?ID = 3123>
Methodology Calculate as:
Numerator: Number of SMEs.
Denominator: Total number of enterprises.
Multiply by 100.
Unit Percentage
Data Sources Data can be collected through local, regional, or national business registration
/ Relevant data.
Databases
SDG Reference(s) SDG Indicator 9.3.1: Percentage of small-scale industries with a total industry value
added.
Verification Check data source.
Guidance
NOTE:
Upper limit for an SME is 250 employees.
DATA VALUE:
Expected KPI value should be more than 95 per cent.
48 U4SSC KPIs Verification Manual-A guide for verifiers