Page 21 - Smart public health emergency management and ICT implementations - A U4SSC deliverable on city platforms
P. 21
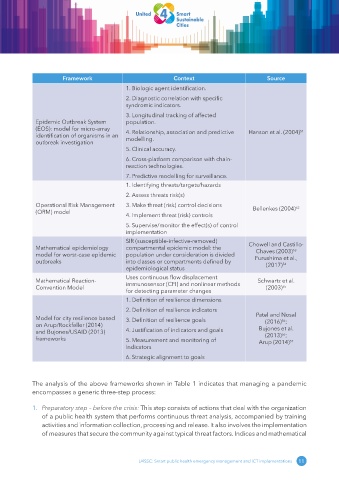
Framework Context Source
1. Biologic agent identification.
2. Diagnostic correlation with specific
syndromic indicators.
3. Longitudinal tracking of affected
Epidemic Outbreak System population.
(EOS): model for micro-array 4. Relationship, association and predictive Hanson et al. (2004) 51
identification of organisms in an modelling.
outbreak investigation
5. Clinical accuracy.
6. Cross-platform comparison with chain-
reaction technologies.
7. Predictive modelling for surveillance.
1. Identifying threats/targets/hazards
2. Assess threats risk(s)
Operational Risk Management 3. Make threat (risk) control decisions Bellenkes (2004) 52
(ORM) model
4. Implement threat (risk) controls
5. Supervise/monitor the effect(s) of control
implementation
SIR (susceptible-infective-removed)
Mathematical epidemiology compartmental epidemic model: the Chowell and Castillo-
Chaves (2003)
53
model for worst-case epidemic population under consideration is divided Furushima et al.,
outbreaks into classes or compartments defined by (2017) 54
epidemiological status
Uses continuous flow displacement
Mathematical Reaction- immunosensor (CFI) and nonlinear methods Schwartz et al.
Convention Model (2003) 55
for detecting parameter changes
1. Definition of resilience dimensions
2. Definition of resilience indicators
Model for city resilience based 3. Definition of resilience goals Patel and Nosal
(2016) ;
56
on Arup/Rockfeller (2014) Bujones et al.
and Bujones/USAID (2013) 4. Justification of indicators and goals (2013) ;
56
frameworks 5. Measurement and monitoring of Arup (2014) 57
Indicators
6. Strategic alignment to goals
The analysis of the above frameworks shown in Table 1 indicates that managing a pandemic
encompasses a generic three-step process:
1. Preparatory step – before the crisis: This step consists of actions that deal with the organization
of a public health system that performs continuous threat analysis, accompanied by training
activities and information collection, processing and release. It also involves the implementation
of measures that secure the community against typical threat factors. Indices and mathematical
U4SSC: Smart public health emergency management and ICT implementations 11