Page 49 - U4SSC Factsheet, Mashhad, Iran (Islamic Republic of), September 2021
P. 49
Mashhad Initiative
• The Mashhad initiative has had successes in the implementation of technology projects. These
projects are summarized in the Appendix. The Mashhad Initiative as reviewed is focused mainly
on technology implementation and projects. As an improvement to the Initiative, Mashhad
should provide a clear horizon and systematic plans through taking into account the variety of
different aspects involved in any smart city programme.
36
• Comparison with the good practices of smart cities elsewhere (e.g., Amsterdam, Moscow or
Barcelona), where there is a clear linkage from strategy, goals and targets to projects, and
thereafter monitoring and measurement is recommended so that the Initiative can be refined.
• As a further improvement to the initiative, Mashhad should also link sustainability goals and
targets to the outcomes of technology projects, and to the overall strategic plan of the Initiative.
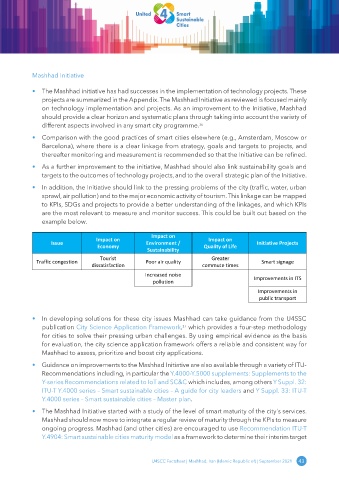
• In addition, the Initiative should link to the pressing problems of the city (traffic, water, urban
sprawl, air pollution) and to the major economic activity of tourism. This linkage can be mapped
to KPIs, SDGs and projects to provide a better understanding of the linkages, and which KPIs
are the most relevant to measure and monitor success. This could be built out based on the
example below.
Impact on
Impact on Impact on
Issue Environment / Initiative Projects
Economy Quality of Life
Sustainability
Tourist Greater
Traffic congestion Poor air quality Smart signage
dissatisfaction commute times
Increased noise
Improvements in ITS
pollution
Improvements in
public transport
• In developing solutions for these city issues Mashhad can take guidance from the U4SSC
publication City Science Application Framework, which provides a four-step methodology
37
for cities to solve their pressing urban challenges. By using empirical evidence as the basis
for evaluation, the city science application framework offers a reliable and consistent way for
Mashhad to assess, prioritize an d boost city application s.
• Guidance on improvements to the Mashhad Initiative are also available through a variety of ITU-
Recommendations including, in particular the Y.4000-Y.5000 supplements: Supplements to the
Y-series Recommendations related to IoT and SC&C which includes, among others Y Suppl. 32:
ITU-T Y.4000 series – Smart sustainable cities – A guide for city leaders and Y Suppl. 33: ITU-T
Y.4000 series – Smart sustainable cities – Master plan.
• The Mashhad Initiative started with a study of the level of smart maturity of the city's services.
Mashhad should now move to integrate a regular review of maturity through the KPIs to measure
ongoing progress. Mashhad (and other cities) are encouraged to use Recommendation ITU-T
Y.4904: Smart sustainable cities maturity model as a framework to determine their interim target
U4SCC Factsheet | Mashhad, Iran (Islamic Republic of) | September 2021 43