Page 33 - U4SSC Compendium of survey results on integrated digital solutions for city platforms around the world
P. 33
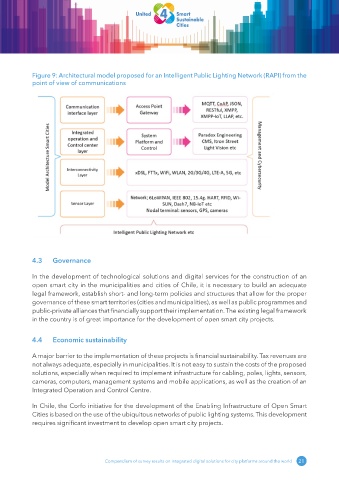
Figure 9: Architectural model proposed for an Intelligent Public Lighting Network (RAPI) from the
point of view of communications
4.3 Governance
In the development of technological solutions and digital services for the construction of an
open smart city in the municipalities and cities of Chile, it is necessary to build an adequate
legal framework, establish short- and long-term policies and structures that allow for the proper
governance of these smart territories (cities and municipalities), as well as public programmes and
public-private alliances that financially support their implementation. The existing legal framework
in the country is of great importance for the development of open smart city projects.
4.4 Economic sustainability
A major barrier to the implementation of these projects is financial sustainability. Tax revenues are
not always adequate, especially in municipalities. It is not easy to sustain the costs of the proposed
solutions, especially when required to implement infrastructure for cabling, poles, lights, sensors,
cameras, computers, management systems and mobile applications, as well as the creation of an
Integrated Operation and Control Centre.
In Chile, the Corfo initiative for the development of the Enabling Infrastructure of Open Smart
Cities is based on the use of the ubiquitous networks of public lighting systems. This development
requires significant investment to develop open smart city projects.
Compendium of survey results on integrated digital solutions for city platforms around the world 21