Page 36 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2021
P. 36
2.2 Automatic concept acquisition patient’s body and the transmitter sends those sounds to a
remotely located receiver [3]. A doctor can operate the
A concept is a mental representation of a category stored in receiver to listen to or record sounds coming from various
memory. It is a set of information that a category points to, parts of the patient’s body. The current prototype has
and it consists of what is known about that category. For eighteen acoustic channels and one Electrocardiogram (ECG)
example, the concept of “cats” that humans hold is not channel. In addition to the frequency range commonly used
limited to the shape or form of cats. It is rather an integrated in conventional auscultation, this system is designed to
abstraction of various aspects of cats, such as the sounds they capture other frequency bands to acquire richer
emit (meowing, etc.), their behavior, the feel of their fur, and multidimensional information about the patient.
the language used to express such aspects. Therefore, a
concept can be acquired by observing a set of attributes in
the same category through different types of media
information or modalities, and it can be understood as an
abstract form independent of those different modalities. The
abstract form is thus expressed as coordinates in a common
conceptual space. Toward Artificial Intelligence (AI) that
understands concepts like humans, cross-media processing
technologies based on deep learning are used to develop a
system that autonomously acquires concepts without having
to be trained with correct answers. By focusing on the fact
that different types of media information originating from
the same thing appear not in a random manner but with
specific relationships, the system autonomously learns
concepts through the co-occurrence of different types of Figure 3 – Tele-stethoscope
media information. Figure 2 shows that the proposed system
is trained with a data set consisting of English, Hindi, and The cross-media processing technologies will bring about
Japanese speech captions for a common image set. The “AI-auscultation” that analyzes and diagnoses a patient’s
extracted features of the related image and sounds are internal physical condition by listening to body sounds
learned to be located closer together than unrelated ones in captured by the tele-stethoscope. For example, a method
the common embedding space. As a result, the system based on a conditional sequence-to-sequence caption
automatically acquires translation knowledge between the generator can automatically convert the body sounds into
three languages using images as pivots. [2]. sentences that describe the sounds’ origins such as “The
heart sounds are abnormal. There may be a problem with one
of the heart valves.” The amount of information contained in
the output can be controlled by a “specificity” parameter.
Visualization of physical states generated from the body
sounds is also being developed as another example of AI-
auscultation.
3. LANGUAGE ACQUISITION IN INFANTS AND
CHILDREN
Do human infants autonomously learn from the co-
occurrence of phenomena in the natural world? For infants,
communication is an important means of recognizing objects
and promoting the acquisition of knowledge, concepts, and
Figure 2 – Cross-lingual translation knowledge acquisition vocabulary. Infants accumulate various types of knowledge
from information obtained from the surrounding
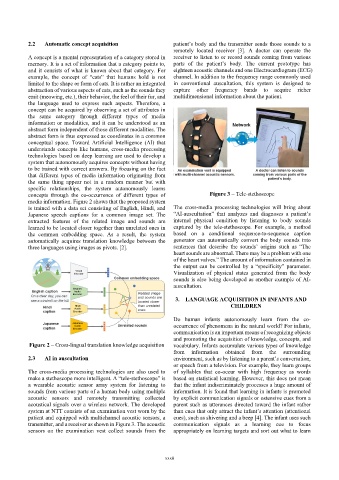
2.3 AI in auscultation environment, such as by listening to a parent’s conversation,
or speech from a television. For example, they learn groups
The cross-media processing technologies are also used to of syllables that co-occur with high frequency as words
make a stethoscope more intelligent. A “tele-stethoscope” is based on statistical learning. However, this does not mean
a wearable acoustic sensor array system for listening to that the infant indiscriminately processes a huge amount of
sounds from various parts of a human body using multiple information. It is found that learning in infants is promoted
acoustic sensors and remotely transmitting collected by explicit communication signals or ostensive cues from a
acoustical signals over a wireless network. The developed parent such as utterances directed toward the infant rather
system at NTT consists of an examination vest worn by the than cues that only attract the infant’s attention (attentional
patient and equipped with multichannel acoustic sensors, a cues), such as shivering and a beep [4]. The infant uses such
transmitter, and a receiver as shown in Figure 3. The acoustic communication signals as a learning cue to focus
sensors on the examination vest collect sounds from the appropriately on learning targets and sort out what to learn
– xxxii –