Page 126 - Kaleidoscope Academic Conference Proceedings 2021
P. 126
2021 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
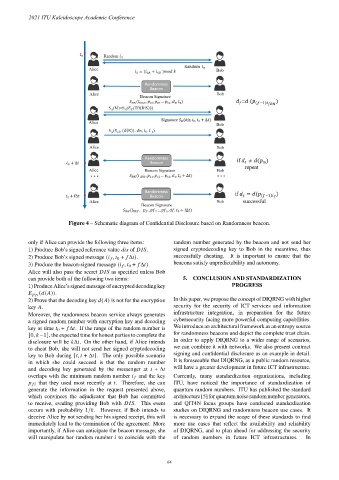
Figure 4 – Schematic diagram of Confidential Disclosure based on Randomness beacon.
only if Alice can provide the following three items: random number generated by the beacon and not send her
1) Produce Bob’s signed reference value of . signed cryptodecoding key to Bob in the meantime, thus
2) Produce Bob’s signed message ( , 0 + Δ ). successfully cheating. It is important to ensure that the
3) Produce the beacon-signed message ( , 0 + Δ ). beacons satisfy unpredictability and autonomy.
Alice will also pass the secret as specified unless Bob
can provide both of the following two items: 5. CONCLUSION AND STANDARDIZATION
1) Produce Alice’s signed message of encrypted decoding key PROGRESS
( ( )).
2) Prove that the decoding key ( ) is not for the encryption In this paper, we propose the concept of DIQRNG with higher
key . security for the security of ICT services and information
Moreover, the randomness beacon service always generates infrastructure integration, in preparation for the future
cybersecurity facing more powerful computing capabilities.
a signed random number with encryption key and decoding
We introduce an architectural framework as an entropy source
key at time 0 + Δ . If the range of the random number is
for randomness beacons and depict the complete trust chain.
[0, −1], the expected time for honest parties to complete the
In order to apply DIQRNG to a wider range of scenarios,
disclosure will be Δ . On the other hand, if Alice intends
we can combine it with networks. We also present contract
to cheat Bob, she will not send her signed cryptodecoding
signing and confidential disclosure as an example in detail.
key to Bob during [ , + Δ ]. The only possible scenario
It is foreseeable that DIQRNG, as a public random resource,
in which she could succeed is that the random number
will have a greater development in future ICT infrastructure.
and decoding key generated by the messenger at + Δ
overlaps with the minimum random number and the key Currently, many standardization organizations, including
that they used most recently at . Therefore, she can ITU, have noticed the importance of standardization of
generate the information in the request presented above, quantum random numbers. ITU has published the standard
which convinces the adjudicator that Bob has committed architecture [5] for quantum noise random number generators,
to receive, evading providing Bob with . This event and QIT4N focus groups have conducted standardization
occurs with probability 1/ . However, if Bob intends to studies on DIQRNG and randomness beacon use cases. It
deceive Alice by not sending her his signed receipt, this will is necessary to expand the scope of these standards to find
immediately lead to the termination of the agreement. More more use cases that reflect the availability and reliability
importantly, if Alice can anticipate the beacon message, she of DIQRNG, and to plan ahead for addressing the security
will manipulate her random number to coincide with the of random numbers in future ICT infrastructures. In
– 64 –