Page 54 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 54
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
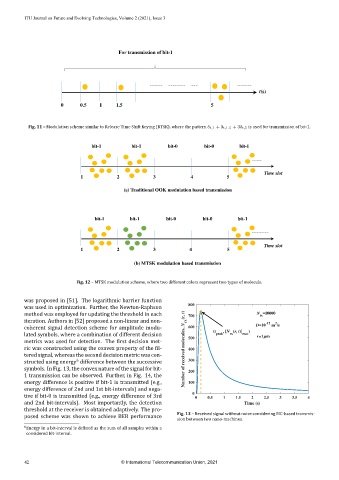
For transmission of bit-1
t(s)
0 0.5 1 1.5 5
Fig. 11 – Modulation scheme similar to Release Time Shift Keying (RTSK), where the pattern δ t,1 + δ t,1.5 + 3δ t,5 is used for transmission of bit‑1.
bit-1 bit-1 bit-0 bit-0 bit-1
Time slot
1 2 3 4 5
(a) Traditional OOK modulation based transmission
bit-1 bit-1 bit-0 bit-0 bit-1
Time slot
1 2 3 4 5
(b) MTSK modulation based transmission
Fig. 12 – MTSK modulation scheme, where two different colors represent two types of molecule.
was proposed in [51]. The logarithmic barrier function
was used in optimization. Further, the Newton‑Raphson 800
method was employed for updating the threshold in each 700 N =10000
tx
iteration. Authors in [52] proposed a non‑linear and non‑ -12 2
coherent signal detection scheme for amplitude modu‑ 600 (t , [N (r, t)] ) D=10 m /s
lated symbols, where a combination of different decision 500 peak rx max r=1 m
metrics was used for detection. The irst decision met‑
ric was constructed using the convex property of the il‑ Number of received molecules, N rx (r, t) 400
tered signal, whereas the second decision metric was con‑
6
structed using energy difference between the successive 300
symbols. In Fig. 13, the convex nature of the signal for bit‑ 200
1 transmission can be observed. Further, in Fig. 14, the
energy difference is positive if bit‑1 is transmitted (e.g., 100
energy difference of 2nd and 1st bit‑intervals) and nega‑
0
tive if bit‑0 is transmitted (e.g., energy difference of 3rd 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
and 2nd bit‑intervals). Most importantly, the detection Time (s)
threshold at the receiver is obtained adaptively. The pro‑
posed scheme was shown to achieve BER performance Fig. 13 – Received signal without noise considering MC‑based transmis‑
sion between two nano‑machines.
6 Energy in a bit‑interval is de ined as the sum of all samples within a
considered bit‑interval.
42 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021