Page 126 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3 – Internet of Bio-Nano Things for health applications
P. 126
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 3
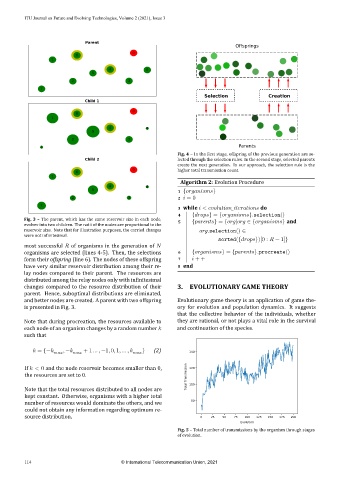
Parent
Offsprings
0
6
1
4
8
5
3
2
7
Selection Creation
Child 1
0
6
1
4
8
5
2 3
Parents
7
Fig. 4 – In the irst stage, offspring of the previous generation are se‑
lected through the selection rules. In the second stage, selected parents
Child 2
create the next generation. In our approach, the selection rule is the
higher total transmission count.
0
6
1
Algorithm 2: Evolution Procedure
4
8
5 1 { }
2 = 0
2 3
3 while < _ do
7
4 { } = { }.selection()
Fig. 3 – The parent, which has the same reservoir size in each node, 5 { } = { | ∈ { } and
evolves into two children. The radii of the nodes are proportional to the
reservoir size. Note that for illustration purposes, the carried changes .selection() ∈
were not in initesimal.
sorted({ })[0 ∶ − 1]}
most successful of organisms in the generation of
organisms are selected (lines 4‑5). Then, the selections 6 { } = { }.procreate()
form their offspring (line 6). The nodes of these offspring 7 + +
have very similar reservoir distribution among their re‑ 8 end
lay nodes compared to their parent. The resources are
distributed among the relay nodes only with in initesimal
changes compared to the resource distribution of their 3. EVOLUTIONARY GAME THEORY
parent. Hence, suboptimal distributions are eliminated,
and better nodes are created. A parent with two offspring Evolutionary game theory is an application of game the‑
is presented in Fig. 3. ory for evolution and population dynamics. It suggests
that the collective behavior of the individuals, whether
Note that during procreation, the resources available to they are rational, or not plays a vital role in the survival
each node of an organism changes by a random number and continuation of the species.
such that
= {− , − + 1 … , −1, 0, 1, … , } (2) 140
If < 0 and the node reservoir becomes smaller than 0, 120
the resources are set to 0. Total Transmission
Note that the total resources distributed to all nodes are 100
kept constant. Otherwise, organisms with a higher total
number of resources would dominate the others, and we 80
could not obtain any information regarding optimum re‑
source distribution. 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Evolution
Fig. 5 – Total number of transmissions by the organism through stages
of evolution.
114 © International Telecommunication Union, 2021