Page 81 - ITU Journal Future and evolving technologies – Volume 2 (2021), Issue 2
P. 81
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 2 (2021), Issue 2
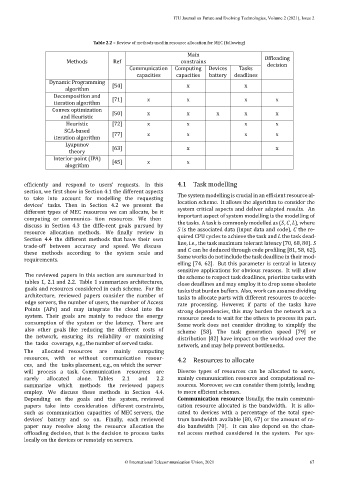
Table 2.2 – Review of methods used in resource allocation for MEC (following)
Main
Methods Ref constrains Of loading
decision
Communication Computing Devices Tasks
capacities capacities battery deadlines
Dynamic Programming
algorithm [54] x x
Decomposition and [71] x x x x
iteration algorithm
Convex optimization [50] x x x x x
and Heuristic
Heuristic [72] x x x x
SCA‑based
iteration algorithm [77] x x x x
Lyapunov [63] x x
theory
Interior‑point (IPA)
alogrithm [45] x x
ef iciently and respond to users’ requests. In this 4.1 Task modelling
section, we irst show in Section 4.1 the different aspects
The system modelling is crucial in an ef icient resource al‑
to take into account for modelling the requesting
location scheme. It allows the algorithm to consider the
devices’ tasks. Then in Section 4.2 we present the
system critical aspects and deliver adapted results. An
different types of MEC resources we can allocate, be it
important aspect of system modelling is the modelling of
computing or communica‑ tion resources. We then
the tasks. A task is commonly modelled as (S, C, L), where
discuss in Section 4.3 the diffe-rent goals pursued by
S is the associated data (input data and code), C the re‑
resource allocation methods. We inally review in
quired CPU cycles to achieve the task and L the task dead‑
Section 4.4 the different methods that have their own line, i.e., the task maximum tolerant latency [70, 68, 80]. S
trade‑off between accuracy and speed. We discuss
and C can be deduced through code pro iling [81, 58, 62].
these methods according to the system scale and
Some works do not include the task deadline in their mod‑
requirements.
elling [74, 62]. But this parameter is central in latency
sensitive applications for obvious reasons. It will allow
The reviewed papers in this section are summarized in
the scheme to respect task deadlines, prioritize tasks with
tables 1, 2.1 and 2.2. Table 1 summarizes architectures,
close deadlines and may employ it to drop some obsolete
goals and resources considered in each scheme. For the
tasks that burden buffers. Also, work can assume dividing
architecture, reviewed papers consider the number of
tasks to allocate parts with different resources to accele-
edge servers, the number of users, the number of Access
rate processing. However, if parts of the tasks have
Points (APs) and may integrate the cloud into the
strong dependencies, this may burden the network as a
system. Their goals are mainly to reduce the energy
resource needs to wait for the others to process its part.
consumption of the system or the latency. There are Some work does not consider dividing to simplify the
also other goals like reducing the different costs of
scheme [58]. The task generation speed [79] or
the network, ensuring its reliability or maximizing
distribution [82] have impact on the workload over the
the tasks coverage, e.g., the number of served tasks. network, and may help prevent bottlenecks.
The allocated resources are mainly computing
resources, with or without communication resour- 4.2 Resources to allocate
ces, and the tasks placement, e.g., on which the server
will process a task. Communication resources are Diverse types of resources can be allocated to users,
rarely allocated alone. Tables 2.1 and 2.2 mainly communication resource and computational re‑
summarize which methods the reviewed papers sources. Moreover, we can consider them jointly, leading
employ. We discuss these methods in Section 4.4. to more ef icient schemes.
Depending on the goals and the system, reviewed Communication resource Usually, the main communi‑
papers take into consideration different constraints, cation resource allocated is the bandwidth. It is allo‑
such as communication capacities of MEC servers, the cated to devices with a percentage of the total spec‑
devices’ battery and so on. Finally, each reviewed trum bandwidth available [80, 67] or the amount of ra‑
paper may resolve along the resource allocation the dio bandwidth [70]. It can also depend on the chan‑
of loading decision, that is the decision to process tasks nel access method considered in the system. For sys‑
locally on the devices or remotely on servers.
© International Telecommunication Union, 2021 67