Page 37 - U4SSC Blockchain for smart sustainable cities
P. 37
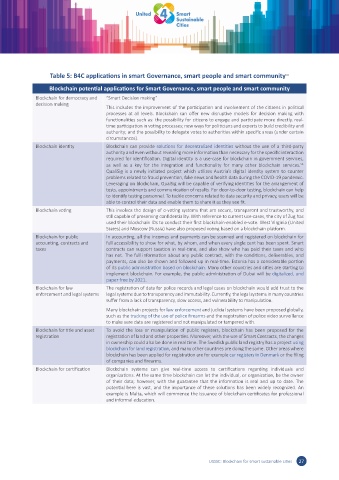
Table 5: B4C applications in smart Governance, smart people and smart community 50
Blockchain potential applications for Smart Governance, smart people and smart community
Blockchain for democracy and “Smart Decision making”
decision making
This includes the improvement of the participation and involvement of the citizens in political
processes at all levels. Blockchain can offer new disruptive models for decision making with
functionalities such as: the possibility for citizens to engage and participate more directly, real-
time participation in voting processes; new ways for politicians and experts to build credibility and
authority; and the possibility to delegate votes to authorities within specific areas (under certain
circumstances).
Blockchain identity Blockchain can provide solutions for decentralized identities without the use of a third-party
authority and even without revealing more information than necessary for the specific interaction
required for identification. Digital identity is a use-case for blockchain in government services,
51
as well as a key for the integration and functionality for many other blockchain services.
QualiSig is a newly initiated project which utilizes Austria’s digital identity system to counter
problems related to fraud prevention, fake news and health data during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Leveraging on blockchain, QualSig will be capable of verifying identities for the arrangement of
tests, appointments and communication of results. For door-to-door testing, blockchain can help
to identify testing personnel. To tackle concerns related to data security and privacy, users will be
able to control their data and enable them to share it as they see fit.
Blockchain voting This involves the design of e-voting systems that are secure, transparent and trustworthy, and
still capable of preserving confidentiality. With reference to current use-cases, the city of Zug has
used their blockchain IDs to conduct their first blockchain-enabled e-vote. West Virginia (United
States) and Moscow (Russia) have also proposed voting based on a blockchain platform.
Blockchain for public In accounting, all the incomes and payments can be scanned and registered on blockchain for
accounting, contracts and full accessibility to show for what, by whom, and when every single cent has been spent. Smart
taxes contracts can support taxation in real-time, and also show who has paid their taxes and who
has not. The full information about any public contract, with the conditions, deliverables, and
payments, can also be shown and followed up in real-time. Estonia has a considerable portion
of its public administration based on blockchain. Many other countries and cities are starting to
implement blockchain. For example, the public administration of Dubai will be digitalized, and
paper free by 2021.
Blockchain for law The registration of data for police records and legal cases on blockchain would add trust to the
enforcement and legal systems legal systems due to transparency and immutability. Currently, the legal systems in many countries
suffer from a lack of transparency, slow access, and vulnerability to manipulation.
Many blockchain projects for law enforcement and judicial systems have been proposed globally,
such as the tracking of the use of police firearms and the registration of police video surveillance
to make sure data are registered and not manipulated or tampered with.
Blockchain for title and asset To avoid the loss or manipulation of public registers, blockchain has been proposed for the
registration registration of land and other properties. Moreover, with the use of Smart Contracts, the changes
in ownership could also be done in real time. The Swedish public land registry has a project using
blockchain for land registration, and many other countries are doing the same. Other areas where
blockchain has been applied for registration are for example car registers in Denmark or the filing
of companies and firearms.
Blockchain for certification Blockchain systems can give real-time access to certifications regarding individuals and
organizations. At the same time blockchain can let the individual, or organization, be the owner
of their data; however, with the guarantee that the information is real and up to date. The
potential here is vast, and the importance of these solutions has been widely recognized. An
example is Malta, which will commence the issuance of blockchain certificates for professional
and informal education.
U4SSC: Blockchain for smart sustainable cities 27