Page 140 - ITU Journal, ICT Discoveries, Volume 3, No. 1, June 2020 Special issue: The future of video and immersive media
P. 140
ITU Journal: ICT Discoveries, Vol. 3(1), June 2020
100 Accordingly, processing times for LCEVC were
measured using the commercial implementations of
90 LCEVC, H.264/AVC and H.265/HEVC, as described
in Section 7.1.2. The encodes and decodes have been
80
performed on a common platform (Intel i9-8950HK
70 @ 2.9GHz).
For each full resolution, the same sequences
60
VMAF 50 mentioned in Section 7.2 were used.
Table 6 reports the average timings for each
resolution for both anchors and LCEVC.
40
Table 6 – Relative encoding and decoding times for LCEVC vs.
30 anchors (anchor ≙ 100%)
20 Base & anchor Resolution Encoder Decoder
codec time time
10
0 600 1,200 1,800 H.264/AVC UHD 32.99% 81.88%
Bit rate (kbps) H.265/HEVC UHD 34.44% 64.24%
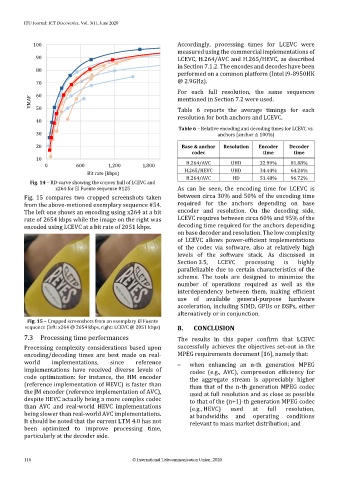
Fig. 14 – RD-curve showing the convex hull of LCEVC and H.264/AVC HD 51.48% 96.72%
x264 for El Fuente sequence #125 As can be seen, the encoding time for LCEVC is
Fig. 15 compares two cropped screenshots taken between circa 30% and 50% of the encoding time
from the above-metioned exemplary sequence #54. required for the anchors depending on base
The left one shows an encoding using x264 at a bit encoder and resolution. On the decoding side,
rate of 2654 kbps while the image on the right was LCEVC requires between circa 60% and 95% of the
encoded using LCEVC at a bit rate of 2051 kbps. decoding time required for the anchors depending
on base decoder and resolution. The low complexity
of LCEVC allows power-efficient implementations
of the codec via software, also at relatively high
levels of the software stack. As discussed in
Section 3.5, LCEVC processing is highly
parallelizable due to certain characteristics of the
scheme. The tools are designed to minimize the
number of operations required as well as the
interdependency between them, making efficient
use of available general-purpose hardware
acceleration, including SIMD, GPUs or DSPs, either
alternatively or in conjunction.
Fig. 15 – Cropped screenshots from an exemplary El Fuente
sequence (left: x264 @ 2654 kbps, right: LCEVC @ 2051 kbps) 8. CONCLUSION
7.3 Processing time performances The results in this paper confirm that LCEVC
Processing complexity considerations based upon successfully achieves the objectives set-out in the
encoding/decoding times are best made on real- MPEG requirements document [16], namely that:
world implementations, since reference – when enhancing an n-th generation MPEG
implementations have received diverse levels of codec (e.g., AVC), compression efficiency for
code optimization: for instance, the HM encoder the aggregate stream is appreciably higher
(reference implementation of HEVC) is faster than than that of the n-th generation MPEG codec
the JM encoder (reference implementation of AVC), used at full resolution and as close as possible
despite HEVC actually being a more complex codec to that of the (n+1)-th generation MPEG codec
than AVC and real-world HEVC implementations (e.g., HEVC) used at full resolution,
being slower than real-world AVC implementations. at bandwidths and operating conditions
It should be noted that the current LTM 4.0 has not relevant to mass market distribution; and
been optimized to improve processing time,
particularly at the decoder side.
118 © International Telecommunication Union, 2020