Page 128 - ITU Journal, Future and evolving technologies - Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1, Inaugural issue
P. 128
ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies, Volume 1 (2020), Issue 1
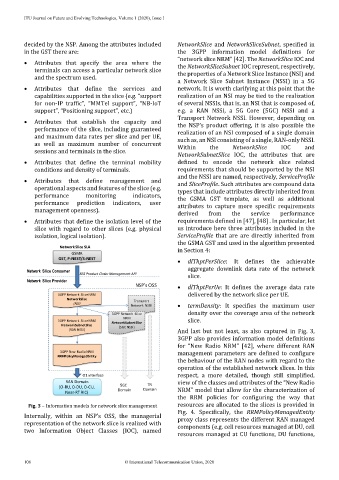
decided by the NSP. Among the attributes included NetworkSlice and NetworkSliceSubnet, specified in
in the GST there are: the 3GPP information model definitions for
“network slice NRM” [42]. The NetworkSlice IOC and
• Attributes that specify the area where the the NetworkSliceSubnet IOC represent, respectively,
terminals can access a particular network slice the properties of a Network Slice Instance (NSI) and
and the spectrum used.
a Network Slice Subnet Instance (NSSI) in a 5G
• Attributes that define the services and network. It is worth clarifying at this point that the
capabilities supported in the slice (e.g. “support realization of an NSI may be tied to the realization
for non-IP traffic”, “MMTel support”, “NB-IoT of several NSSIs, that is, an NSI that is composed of,
support”, “Positioning support”, etc.) e.g. a RAN NSSI, a 5G Core (5GC) NSSI and a
Transport Network NSSI. However, depending on
• Attributes that establish the capacity and the NSP’s product offering, it is also possible the
performance of the slice, including guaranteed realization of an NSI composed of a single domain
and maximum data rates per slice and per UE, such as, an NSI consisting of a single, RAN-only NSSI.
as well as maximum number of concurrent Within the NetworkSlice IOC and
sessions and terminals in the slice.
NetworkSubnetSlice IOC, the attributes that are
• Attributes that define the terminal mobility defined to encode the network slice related
conditions and density of terminals. requirements that should be supported by the NSI
and the NSSI are named, respectively, ServiceProfile
• Attributes that define management and and SliceProfile. Such attributes are compound data
operational aspects and features of the slice (e.g. types that include attributes directly inherited from
performance monitoring indicators, the GSMA GST template, as well as additional
performance prediction indicators, user attributes to capture more specific requirements
management openness).
derived from the service performance
• Attributes that define the isolation level of the requirements defined in [47], [48] . In particular, let
slice with regard to other slices (e.g. physical us introduce here three attributes included in the
isolation, logical isolation). ServiceProfile that are are directly inherited from
the GSMA GST and used in the algorithm presented
Network Slice SLA in Section 4:
GSMA
GST, P-NEST/S-NEST
• dlThptPerSlice: It defines the achievable
aggregate downlink data rate of the network
Network Slice Consumer
BSS Product Order Management API slice.
Network Slice Provider
NSP’s OSS • dlThptPerUe: It defines the average data rate
3GPP Network SliceNRM delivered by the network slice per UE.
NetworkSlice Transport
(NSI)
Network NSSI • termDensity: It specifies the maximum user
density over the coverage area of the network
3GPP Network Slice
NRM
3GPP Network SliceNRM NetworkSubnetSlice slice.
NetworkSubnetSlice (5GC NSSI)
(RAN NSSI) And last but not least, as also captured in Fig. 3,
3GPP also provides information model definitions
for “New Radio NRM” [42], where different RAN
3GPP New Radio NRM management parameters are defined to configure
RRMPolicyManagedEntity
the behaviour of the RAN nodes with regard to the
operation of the established network slices. In this
O1 interface respect, a more detailed, though still simplified,
RAN Domain view of the classes and attributes of the “New Radio
(O-RU, O-DU, O-CU, 5GC TN
Domain Domain NRM” model that allow for the characterization of
Near-RT RIC)
the RRM policies for configuring the way that
Fig. 3 – Information models for network slice management resources are allocated to the slices is provided in
Fig. 4. Specifically, the RRMPolicyManagedEntity
Internally, within an NSP’s OSS, the managerial proxy class represents the different RAN managed
representation of the network slice is realized with components (e.g. cell resources managed at DU, cell
two Information Object Classes (IOC), named
resources managed at CU functions, DU functions,
108 © International Telecommunication Union, 2020