Page 45 - Digital Financial Services security assurance framework
P. 45
leverage these interfaces to attack the system, with successful exploits often having consequences that affect not merely the exploited stakeholders
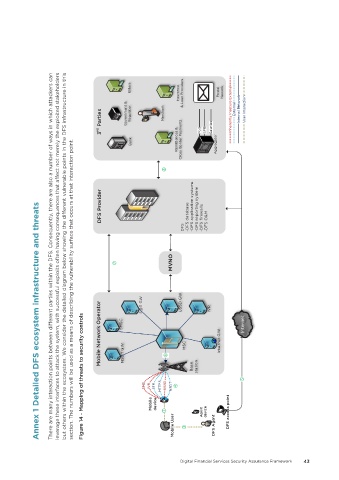
but others within the ecosystem. We consider the detailed diagram below showing the different vulnerable points in the DFS infrastructure in this
There are many interaction points between different parties within the DFS. Consequently, there are also a number of ways in which attackers can
Billers Billers Insurance Insurance & Loan Providers & Loan Providers Postal Postal Postal Nework Nework Nework
3 rd Parties Government & Government & Regulator Regulator Merchant Merchant PoS SME Inherently Insecure External External Internal Network User Interaction
Bank Bank Remittances Remittances Remittances & Remittances & Cross Border Cross Border Cross Border Payments Cross Border Payments Payments Payments Aggregator
section. The numbers will be used as a means of describing the vulnerability surface that occurs at that interaction point.
DFS Provider -DFS application systems -DFS reporting system
Annex 1 Detailed DFS ecosystem infrastructure and threats
DFS -DFS database -DFS firewalls -DFS O&M
MVNO
Mobile Network Operator SMSC SMSC NSDT GW NSDT GW S@T GW S@T GW USSD GW USSD GW MSC MSC IVR IVR Internet GW Internet GW Internet Internet
Figure 14 - Mapping of threats to security controls
station
station
Base
Base
Mobile device Agent device DFS access point
Mobile User DFS Agent
Digital Financial Services Security Assurance Framework 43