Page 20 - Case study: Crime prediction for more agile policing in cities – Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
P. 20
B. Annex
Selected applications of predictive policing and evaluation results
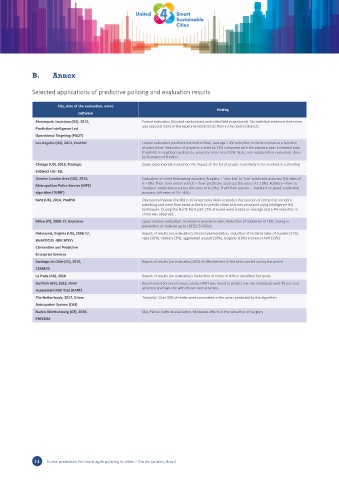
City, date of the evaluation, name
Finding
software
Shreveport, Louisiana (US), 2012, Formal evaluation (blocked randomized controlled field experiment). No statistical evidence that crime
Predictive Intelligence Led was reduced more in the experimental districts than in the control districts
Operational Targeting (PILOT)
Los Angeles (US), 2013, PredPol Formal evaluation (randomized control trial). Average 7.4% reduction in crime volume as a function
of patrol time. Reduction of property crimes by 12% compared with the previous year in treated area
(Foothill); in neighboring districts, property crime rose 0.5%. Note: non-independent evaluation, done
by founders of PredPol
Chicago (US), 2013, Strategic Quasi experimental evaluation. No impact of the list of people most likely to be involved in a shooting
Subjects Litc- SSL
Greater London Area (UK), 2013, Evaluation of crime forecasting accuracy. Burglary – ‘very low’ to ‘low’ predictive accuracy (hit rates of
Metropolitan Police Service (MPS) 0 – 5%). Theft from motor vehicle – ‘low’ predictive accuracy (hit rates of 1-10%). Robbery –‘low’ to
‘medium’ predictive accuracy (hit rates of 0-20%). Theft from person – ‘medium’ to ‘good’ predictive
algorithm (‘MBR’) accuracy (hit rates of 13- 54%).
Kent (UK), 2014, PredPol Operational review. PredPol is 10 times more likely to predict the location of crime than random
patrolling and more than twice as likely to predict crime as boxes produced using intelligence led
techniques. During the North Kent pilot 25% of boxes were visited on average and a 4% reduction in
crime was observed.
Milan (IT), 2008-17, KeyCrime Quasi random evaluation. Increase in clearance rates. Reduction of robberies in 18%. Saving in
prevention of violence up to USD$2.5 million
Richmond, Virginia (US), 2006-17, Report of results (no evaluation). Since implementation, reduction of incident rates of murder (32%),
WebFOCUS -IBM SPSS’s rape (20%), robbery (3%), aggravated assault (18%), burglary (18%) and auto theft (13%).
Clementine and Predictive
Enterprise Services
Santiago de Chile (CL), 2015, Report of results (no evaluation) 89% of effectiveness in the tests carried out by the police
CEAMOS
La Plata (AR), 2018 Report of results (no evaluation). Reduction of crime in 40% in identified hot spots.
Durham (UK), 2013, Harm Royal United Services Institute study. HART was found to predict low-risk individuals with 98 per cent
accuracy and high-risk with 88 per cent accuracy.
Assessment Risk Tool (HART)
The Netherlands, 2017, Crime Trial pilot. Over 30% of thefts were committed in the zones predicted by the algorithm
Anticipation System (CAS)
Baden-Württemberg (GE), 2016, Max Planck Institute evaluation. Moderate effects in the reduction of burglary
PRECOBS
14 Crime prediction for more agile policing in cities – Rio de Janeiro, Brazil