Page 80 - ITU KALEIDOSCOPE, ATLANTA 2019
P. 80
2019 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
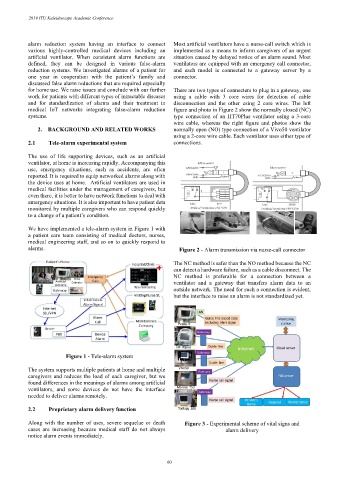
alarm reduction system having an interface to connect Most artificial ventilators have a nurse-call switch which is
various highly-controlled medical devices including an implemented as a means to inform caregivers of an urgent
artificial ventilator. When consistent alarm functions are situation caused by delayed notice of an alarm sound. Most
defined, they can be designed in various false-alarm ventilators are equipped with an emergency call connector,
reduction systems. We investigated alarms of a patient for and each model is connected to a gateway server by a
one year in cooperation with the patient’s family and connector.
discussed false alarm reductions that are required especially
for home use. We raise issues and conclude with our further There are two types of connecters to plug in a gateway, one
work for patients with different types of intractable diseases using a cable with 3 core wires for detection of cable
and for standardization of alarms and their treatment in disconnection and the other using 2 core wires. The left
medical IoT networks integrating false-alarm reduction figure and photo in Figure 2 show the normally closed (NC)
systems. type connection of an HT70Plus ventilator using a 3-core
wire cable, whereas the right figure and photos show the
2. BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORKS normally open (NO) type connection of a Vivo50 ventilator
using a 2-core wire cable. Each ventilator uses either type of
2.1 Tele-alarm experimental system connections.
The use of life supporting devices, such as an artificial
ventilator, at home is increasing rapidly. Accompanying this
use, emergency situations, such as accidents, are often
reported. It is required to equip networked alarms along with
the device uses at home. Artificial ventilators are used in
medical facilities under the management of caregivers, but
even there, it is better to have network functions to deal with
emergency situations. It is also important to have patient data
monitored by multiple caregivers who can respond quickly
to a change of a patient’s condition.
We have implemented a tele-alarm system in Figure 1 with
a patient care team consisting of medical doctors, nurses,
medical engineering staff, and so on to quickly respond to
alarms. Figure 2 - Alarm transmission via nurse-call connector
The NC method is safer than the NO method because the NC
can detect a hardware failure, such as a cable disconnect. The
NC method is preferable for a connection between a
ventilator and a gateway that transfers alarm data to an
outside network. The need for such a connection is evident,
but the interface to raise an alarm is not standardized yet.
Figure 1 - Tele-alarm system
The system supports multiple patients at home and multiple
caregivers and reduces the load of each caregiver, but we
found differences in the meanings of alarms among artificial
ventilators, and some devices do not have the interface
needed to deliver alarms remotely.
2.2 Proprietary alarm delivery function
Along with the number of uses, severe sequelae or death Figure 3 - Experimental scheme of vital signs and
cases are increasing because medical staff do not always alarm delivery
notice alarm events immediately.
– 60 –