Page 119 - ITU KALEIDOSCOPE, ATLANTA 2019
P. 119
ICT for Health: Networks, standards and innovation
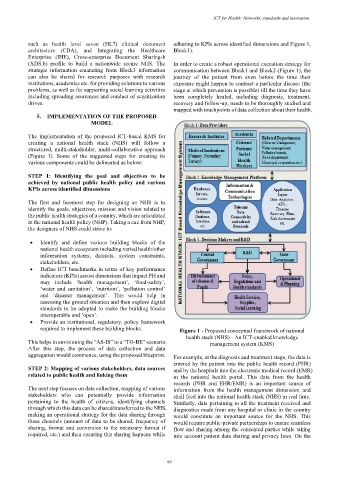
such as health level seven (HL7) clinical document adhering to KPIs across identified dimensions and Figure 1,
architecture (CDA), and Integrating the Healthcare Block1).
Enterprise (IHE), Cross-enterprise Document Sharing-b
(XDS.b) profile to build a nationwide secure NHS. The In order to create a robust operational execution strategy for
strategic information emanating from Block3 information communication between Block1 and Block2 (Figure 1), the
can also be shared for research purposes with research journey of the patient from even before the time their
institutions, academics etc. for providing solutions to various exposure might happen to contract a particular disease (the
problems, as well as for supporting social learning activities stage at which prevention is possible) till the time they have
including spreading awareness and conduct of sensitization been completely healed, including diagnosis, treatment,
drives. recovery and follow-up, needs to be thoroughly studied and
mapped with touchpoints of data collection about their health.
5. IMPLEMENTATION OF THE PROPOSED
MODEL
The implementation of the proposed ICT-based KMS for
creating a national health stack (NHS) will follow a
structured, multi-stakeholder, multi-collaborative approach
(Figure 1). Some of the suggested steps for creating its
various components could be delineated as below:
STEP 1: Identifying the goal and objectives to be
achieved by national public health policy and various
KPIs across identified dimensions
The first and foremost step for designing an NHS is to
identify the goals, objectives, mission and vision related to
the public health strategies of a country, which are articulated
in the national health policy (NHP). Taking a cue from NHP,
the designers of NHS could strive to:
• Identify and define various building blocks of the
national health ecosystem including varied health/other
information systems, datasets, system constraints,
stakeholders, etc.
• Define ICT benchmarks in terms of key performance
indicators (KPIs) across dimensions that impact PH and
may include ‘health management’, ‘food-safety’,
‘water and sanitation’, ‘nutrition’, ‘pollution control’
and ‘disaster management’. This would help in
assessing the ground situation and then explore digital
standards to be adopted to make the building blocks
interoperable and ‘open’.
• Provide an institutional, regulatory, policy framework
required to implement these building blocks. Figure 1 - Proposed conceptual framework of national
health stack (NHS) - An ICT-enabled knowledge
This helps in envisioning the “AS-IS” to a “TO-BE” scenario. management system (KMS)
After this step, the process of data collection and data
aggregation would commence, using the proposed blueprint. For example, at the diagnosis and treatment stage, the data is
entered by the patient into the public health record (PHR)
STEP 2: Mapping of various stakeholders, data sources and by the hospitals into the electronic medical record (EMR)
related to public health and linking them in the national health portal. This data from the health
records (PHR and EHR/EMR) is an important source of
The next step focuses on data collection, mapping of various information from the health management dimension and
stakeholders who can potentially provide information shall feed into the national health stack (NHS) in real time.
pertaining to the health of citizens, identifying channels Similarly, data pertaining to all the treatment received and
through which this data can be shared/transferred to the NHS, diagnostics made from any hospital or clinic in the country
making an operational strategy for the data sharing through would constitute an important source for the NHS. This
these channels (amount of data to be shared, frequency of would require public-private partnerships to ensure seamless
sharing, format and conversion to the necessary format if flow and sharing among the consented parties while taking
required, etc.) and then ensuring this sharing happens while into account patient data sharing and privacy laws. On the
– 99 –