Page 90 - Proceedings of the 2018 ITU Kaleidoscope
P. 90
2018 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
Service requirements
Virtual Network Operator (VNO)
QoS requirements Functions, protocols
Application Service
Provider
Control & management Analysis
Network resource request
Various services Network slices
Autonomous cars
SNS
Sensors & actuators
Network resource
allocation/adjustment
Resource controller of substrate network
IoT devices Core network Cloud
Edge network Infrastructure Provider
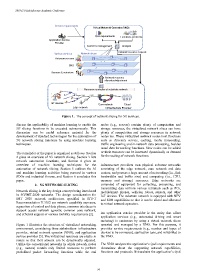
Figure 1. The concept of network slicing for 5G services.
discuss the applicability of machine learning to enable the nodes (e.g., servers) contain plenty of computation and
5G slicing functions to be executed autonomously. This storage resources, the virtualized network slices can have
discussion can be useful reference material for the plenty of computation and storage resources in network
development of standard technologies for the automation of nodes too. These virtualized network nodes host functions
5G network slicing functions by using machine learning such as directory service, caching, media transcoding,
techniques. traffic engineering and in-network data processing, besides
usual data forwarding functions. New nodes can be added
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section or their resources can be increased dynamically as demand
2 gives an overview of 5G network slicing. Section 3 lists for the scaling of network functions.
network automation functions, and Section 4 gives an
overview of machine learning techniques for the Infrastructure providers own physical substrate networks
automation of network slicing. Section 5 outlines the AI consisting of the edge network, core network and data
and machine learning activities being pursued in various centers, and possess a huge amount of networking (i.e., link
SDOs and industrial forums, and Section 6 concludes this bandwidths and buffer size) and computing (i.e., CPU,
paper. memory and storage) resources. Edge networks are
2. 5G NETWORK SLICING composed of equipment for collecting, processing, and
transmitting data to/from various terminals such as PCs,
Network slicing is the key design concept being introduced mobile/smart phones, vehicles, robots, sensors, and other
in 5G/IMT-2020 networks. The design consideration for IoT devices. The substrate network is equipped with NFV
IMT 2020 network architecture specified in ITU-T and SDN capabilities so that it can be sliced and allocated
Recommendation Y.3102 are network capability exposure, to virtual network operators.
separation of control and data planes, common interfaces to
support access network agnostic common core network,
and efficient support of various mobility requirements [2]. An application service provider is the entity that offers
application services (e.g., automated driving and smart
metering) to customers by using a virtual network slices
Figure 1 illustrates the structure of virtualized networking operated and managed by a VNO. For this purpose, it
environment, considering three stakeholders: infrastructure provides service requirements (e.g., number and types of
provider, virtual network operator (VNO), and application devices to be connected, application type, and reliability) to
service provider [5]. The virtualized resources are elastic in the VNO.
nature so that their amount can be dynamically adjusted.
Unlike the conventional networks in which network nodes The VNO analyses the application’s QoS requirements and
(e.g., routers) contain only limited resources to perform determines about the supporting network capabilities,
predefined packet forwarding functions while the end functions and protocols. It translates the application’s QoS
– 74 –