Page 93 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 93
Trust in ICT 1
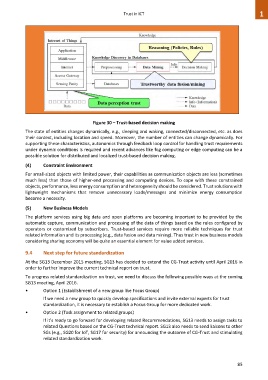
Figure 30 – Trust-based decision making
The state of entities changes dynamically, e.g., sleeping and waking, connected/disconnected, etc. as does
their context, including location and speed. Moreover, the number of entities can change dynamically. For
supporting these characteristics, autonomics through feedback loop control for handling trust requirements
under dynamic conditions is required and recent advances like fog computing or edge computing can be a
possible solution for distributed and localized trust-based decision making.
(4) Constraint Environment
For small-sized objects with limited power, their capabilities as communication objects are less (sometimes
much less) than those of higher-end processing and computing devices. To cope with these constrained
objects, performance, less energy consumption and heterogeneity should be considered. Trust solutions with
lightweight mechanisms that remove unnecessary loads/messages and minimize energy consumption
become a necessity.
(5) New Business Models
The platform services using big data and open platforms are becoming important to be provided by the
automatic capture, communication and processing of the data of things based on the rules configured by
operators or customized by subscribers. Trust-based services require more reliable techniques for trust
related information and its processing (e.g., data fusion and data mining). Thus trust in new business models
considering sharing economy will be quite an essential element for value added services.
9.4 Next step for future standardization
At the SG13 December 2015 meeting, SG13 has decided to extend the CG-Trust activity until April 2016 in
order to further improve the current technical report on trust.
To progress related standardization on trust, we need to discuss the following possible ways at the coming
SG13 meeting, April 2016.
• Option 1 (Establishment of a new group like Focus Group)
If we need a new group to quickly develop specifications and invite external experts for trust
standardization, it is necessary to establish a Focus Group for more dedicated work.
• Option 2 (Task assignment to related groups)
If it’s ready to go forward for developing related Recommendations, SG13 needs to assign tasks to
related Questions based on the CG-Trust technical report. SG13 also needs to send liaisons to other
SGs (e.g., SG20 for IoT, SG17 for security) for announcing the outcome of CG-Trust and stimulating
related standardization work.
85