Page 62 - Trust in ICT 2017
P. 62
1 Trust in ICT
The social IoT [44] transforms smart objects into social entities which are capable of bridging human-to-
object interactions. In this way, a social network of objects is created by intelligent
reasoning/recommendation mechanisms. These mechanisms extract the social knowledge hidden in the rich
profiles of humans and services maintained by various social network services [44].The paradigm of Cyber-
Physical-Social Systems (CPSS) [45] [46] has recently gained momentum as an environment that combines
knowledge from various smart spaces to form an ecosystem, in which intelligence and reasoning about the
social aspects that are embedded in human behaviour in smart spaces act as the glue for integrating physical,
cyber and social worlds (See Figure 27).
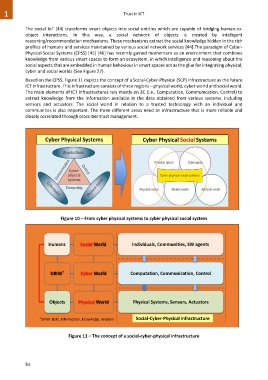
Based on the CPSS, Figure 11 depicts the concept of a Social-Cyber-Physical (SCP) infrastructure as the future
ICT infrastructure. This infrastructure consists of three regions – physical world, cyber world and social world.
The main elements of ICT infrastructures rely mostly on 3C (i.e., Computation, Communication, Control) to
extract knowledge from the information available in the data obtained from various systems, including
sensors and actuators. The social world in relation to a trusted technology with an individual and
communities is also important. The three different areas need an infrastructure that is more reliable and
closely correlated through cross-tier trust management.
Figure 10 – From cyber physical systems to cyber physical social system
Humans Social World Individuals, Communities, SW agents
DIKW * Cyber World Computation, Communication, Control
Objects Physical World Physical Systems, Sensors, Actuators
* DIKW: Data, Information, Knowledge, Wisdom Social-Cyber-Physical Infrastructure
Figure 11 – The concept of a social-cyber-physical infrastructure
54