Page 98 - Proceedings of the 2017 ITU Kaleidoscope
P. 98
2017 ITU Kaleidoscope Academic Conference
3.2. Motivations and incentives for data use 3.3. Data collection and monitoring
During the preparation stage, individuals’ motivation for From the preparation stage, once individuals have
collecting and using data are considered. At this stage established the motivations for monitoring and collecting
individuals also make decisions regarding not only the data data, and having identified the relevant tools, they progress
that they intend to monitor, but also the associated tools that to undertake the actual collection and recording of the data.
they use for the monitoring.
From the participants in the survey the use of fitness /
In economic theory and social psychology, motivations are activity trackers is observed at 18.75% for daily use, 6.25%
typically considered to either be intrinsic or extrinsic [26]. for weekly use, 2.08% for monthly use, 10.42% for seldom
In the case of intrinsic motivation, the benefits of use, and 62.5% for never used. While the use of fitness /
undertaking an action accrue directly and immediately to activity trackers is specifically for tracking personal health
the individual in a form of enjoyment-based or obligation- metrics, increasingly individuals are also making use of the
based satisfaction. Extrinsic motivations on the other hand smart phone apps and smart watches for monitoring and
involve an indirect reward, such as money. While the terms tracking of personal health metrics. From the survey 87.5%
“motivation” and “incentive” are sometimes used of the people indicated that they never used smart watches,
interchangeably, a distinction is sometimes made where while 10.42% and 2.08% use their smart watches daily and
motivations are considered more intrinsic while incentives weekly respectively. The use of smart phones is high as
are more extrinsic to individuals [27]. There is an interplay expected at 95.83% of individual claiming daily use, 2.08%
between motivations and incentives towards influencing for seldom use and 2.08% for having never used a smart
individuals decisions and actions, where phenomenon such phone before. This captures the general use of smart phones
a “crowding out” can occur due to extrinsic incentives by the participants and not just specifically for self tracking
eroding intrinsic motivations [26]. There has been research and monitoring.
undertaken that explores incentivizing individual’s
participation in data related activities, such as participating 3.4. Data utility, sharing, and social sense-making
in online surveys [28], however there is a gap in literature
on incentives for data contribution in the context of the The conversion of monitored and collected individual data
sustainable development agenda. into developmental action is decomposed by Li et al into
two distinct processes of integration and reflection [15].
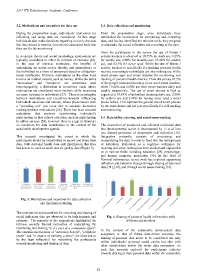
This research investigated the extent to which the Integration primarily consists of processing and
participants would be incentivized to record and share their manipulating the data in order to feed into the next process
data, both personal health data and information that they of reflection. Reflection as a cognitive technique for
had access to, such as water and air quality data (Figure 3). meaning and sense making has been studied and expounded
on in various fields including education [29], psychology,
and human computer interaction [30]. In the field of
Personal Informatics, recent work has explored supporting
reflection and behavior change through sharing of personal
data [31], [32], and through social sense-making [16].
Fig. 3. Motivations and incentives for data collection
and information sharing
The motivations and incentives for recording and sharing of
social indicators data are observed to be both intrinsic and Fig. 4. Sharing of personal health information with
extrinsic. The majority of the respondents highlighted the different stakeholders
intrinsic socially framed motivation of undertaking the
monitoring and sharing “if it’s part of a community effort”.
The extrinsic motivations of “monetary benefit”, “cellphone In the context of the sustainable development data
credit” and “a chance of winning a price” are observed to ecosystem or that of future data-driven societies, the
sharing of personal data needs to be considered not only
be the least influential for motivating the participants
towards monitoring and sharing of data. within individuals’ personal social circles but also with
other stakeholders within the wider data ecosystem. As
such this research explored the participants attitudes
towards sharing of their personal data within the sustainable
– 82 –