Page 48 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 48
2 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
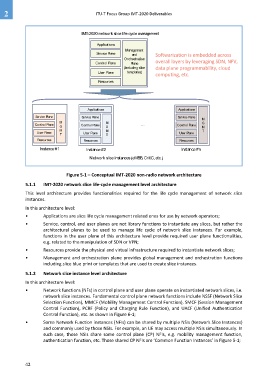
IMT-2020 network slice life-cycle management
Applications
Management
Service Plane and Softwarization is embedded across
Orchestration
Control Plane Plane overall layers by leveraging SDN, NFV,
(including slice data plane programmability, cloud
User Plane templates)
computing, etc.
Resources
Applications Applications
Service Plane Service Plane Service Plane M
M M G
Control Plane G Control Plane G … Control Plane M
M M T
User Plane User Plane User Plane
T T
Resources Resources Resources
Instance #1 Instance #2 Instance #n
Network slice instances (eMBB, CritC, etc.)
Figure 5-1 – Conceptual IMT-2020 non-radio network architecture
5.1.1 IMT-2020 network slice life-cycle management level architecture
This level architecture provides functionalities required for the life cycle management of network slice
instances.
In this architecture level:
• Applications are slice life cycle management related ones for use by network operators;
• Service, control, and user planes are not library functions to instantiate any slices, but rather the
architectural planes to be used to manage life cycle of network slice instances. For example,
functions in the user plane of this architecture level provide required user plane functionalities,
e.g. related to the manipulation of SDN or VPN;
• Resources provide the physical and virtual infrastructure required to instantiate network slices;
• Management and orchestration plane provides global management and orchestration functions
including slice blue print or templates that are used to create slice instances.
5.1.2 Network slice instance level architecture
In this architecture level:
• Network functions (NFs) in control plane and user plane operate on instantiated network slices, i.e.
network slice instances. Fundamental control plane network functions include NSSF (Network Slice
Selection Function), MMCF (Mobility Management Control Function), SMCF (Session Management
Control Function), PCRF (Policy and Charging Rule Function), and UACF (Unified Authentication
Control Function), etc. as shown in Figure 6-1;
• Some Network Function instances (NFIs) can be shared by multiple NSIs (Network Slice Instances)
and commonly used by those NSIs. For example, an UE may access multiple NSIs simultaneously. In
such case, those NSIs share some control plane (CP) NFIs, e.g. mobility management function,
authentication function, etc. Those shared CP NFIs are ‘Common Function Instances’ in Figure 5-1;
42