Page 194 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 194
3 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
FlexE Channel
(75G MAC)
FlexE Client FlexE Client
FlexE Channel
(50G MAC)
FlexE Client FlexE Client
FlexE Channel
(25G MAC)
FlexE Client FlexE Client
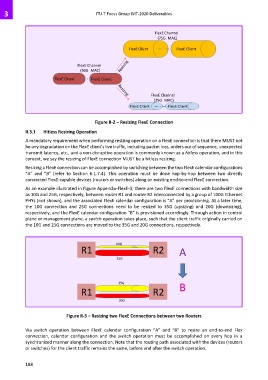
Figure II-2 – Resizing FlexE Connection
II.3.1 Hitless Resizing Operation
A mandatory requirement when performing resizing operation on a FlexE connection is that there MUST not
be any degradation on the FlexE client’s live traffic, including packet loss, orders out of sequence, unexpected
transmit latency, etc., and a non-disruptive operation is commonly known as a hitless operation, and in this
context, we say the resizing of FlexE connection MUST be a hitless resizing.
Resizing a FlexE connection can be accomplished by switching between the two FlexE calendar configurations
“A” and “B” (refer to Section 6.1.7.4). This operation must be done hop-by-hop between two directly
connected FlexE-capable devices (routers or switches) along an existing end-to-end FlexE connection.
As an example illustrated in Figure Appendix-FlexE-3, there are two FlexE connections with bandwidth size
as 10G and 25G, respectively, between router R1 and router R2 interconnected by a group of 100G Ethernet
PHYs (not shown), and the associated FlexE calendar configuration is “A” per provisioning. At a later time,
the 10G connection and 25G connections need to be resized to 35G (upsizing) and 20G (downsizing),
respectively, and the FlexE calendar configuration “B” is provisioned accordingly. Through action in control
plane or management plane, a switch operation takes place, such that the client traffic originally carried on
the 10G and 25G connections are moved to the 35G and 20G connections, respectively.
10G
R1 R2 A
25G
35G B
R1 R2
20G
Figure II-3 – Resizing two FlexE Connections between two Routers
Via switch operation between FlexE calendar configuration “A” and “B” to resize an end-to-end Flex
connection, calendar configuration and the switch operation must be accomplished on every hop in a
synchronized manner along the connection. Note that the routing path associated with the devices (routers
or switches) for the client traffic remains the same, before and after the switch operation.
188