Page 192 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 192
3 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
Appendix II
FlexE
II.1 IP/Ethernet based Mobile Backhaul
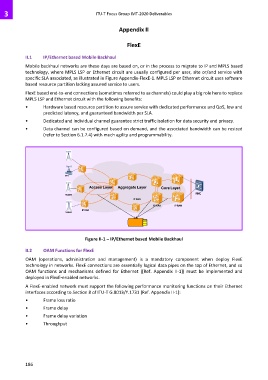
Mobile backhaul networks are these days are based on, or in the process to migrate to IP and MPLS based
technology, where MPLS LSP or Ethernet circuit are usually configured per user, site or/and service with
specific SLA associated, as illustrated in Figure Appendix-FlexE-1. MPLS LSP or Ethernet circuit uses software
based resource partition lacking assured service to users.
FlexE based end-to-end connections (sometimes referred to as channels) could play a big role here to replace
MPLS LSP and Ethernet circuit with the following benefits:
• Hardware based resource partition to assure service with dedicated performance and QoS, low and
predicted latency, and guaranteed bandwidth per SLA.
• Dedicated and individual channel guarantee strict traffic isolation for data security and privacy.
• Data channel can be configured based on demand, and the associated bandwidth can be resized
(refer to Section 6.1.7.4) with much agility and programmability.
BTS
Access Layer Aggregate Layer Core Layer
RNC
NodeB
IP RAN
IP RAN IP RAN
IP RAN
NodeB
Figure II-1 – IP/Ethernet based Mobile Backhaul
II.2 OAM Functions for FlexE
OAM (operations, administration and management) is a mandatory component when deploy FlexE
technology in networks. FlexE connections are essentially logical data pipes on the top of Ethernet, and so
OAM functions and mechanisms defined for Ethernet ([Ref. Appendix II-1]) must be implemented and
deployed in FlexE-enabled networks.
A FlexE-enabled network must support the following performance monitoring functions on their Ethernet
interfaces according to Section 8 of ITU-T G.8013/Y.1731 [Ref. Appendix II-1]:
• Frame loss ratio
• Frame delay
• Frame delay variation
• Throughput
186