Page 158 - ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
P. 158
3 ITU-T Focus Group IMT-2020 Deliverables
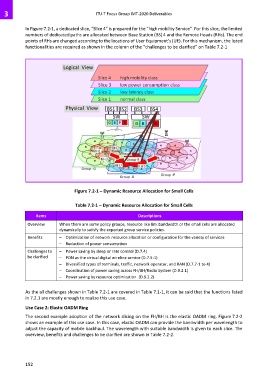
In Figure 7.2-1, a dedicated slice, “Slice 4” is prepared for the “high mobility Service”. For this slice, the limited
numbers of dedicated paths are allocated between Base Station (BS) 4 and the Remote Heads (RHs). The end
points of RHs are changed according to the locations of User Equipment’s (UE). For this mechanism, the listed
functionalities are required as shown in the column of the “challenges to be clarified” on Table 7.2-1
Figure 7.2-1 – Dynamic Resource Allocation for Small Cells
Table 7.2-1 – Dynamic Resource Allocation for Small Cells
Items Descriptions
Overview When there are some policy groups, resource like link bandwidth or the small cells are allocated
dynamically to satisfy the expected group service policies.
Benefits – Optimization of network resource allocation or configuration for the variety of services
– Reduction of power consumption
Challenges to – Power saving by sleep or rate control (D.7.4)
be clarified – PON as the virtual digital wireline service (D.7.5-1)
– Diversified types of terminals, traffic, network operator, and RAN (D.7.7-1 to 4)
– Coordination of power saving across FH/BH/Radio System (D.9.2.1)
– Power saving by resource optimization (D.9.2.2)
As the all challenges shown in Table 7.2-1 are covered in Table 7.1-1, it can be said that the functions listed
in 7.2.1 are mostly enough to realize this use case.
Use Case 2: Elastic OADM Ring
The second example adoption of the network slicing on the FH/BH is the elastic OADM ring. Figure 7.2-2
shows an example of this use case. In this case, elastic OADM can provide the bandwidth per wavelength to
adjust the capacity of mobile backhaul. The wavelength with suitable bandwidth is given to each slice. The
overview, benefits and challenges to be clarified are shown in Table 7.2-2.
152